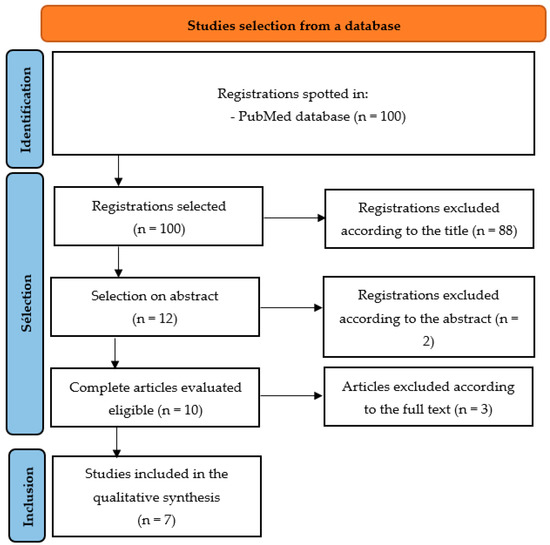
Listeria monocytogenes (
L. monocytogenes) poses a significant threat to food safety due to its ability to cause severe human illness and its resistance to various antibiotics and environmental conditions. This study investigated the prevalence, serotype distribution, virulence gene profiles, and antimicrobial
[...] Read more.
Listeria monocytogenes (
L. monocytogenes) poses a significant threat to food safety due to its ability to cause severe human illness and its resistance to various antibiotics and environmental conditions. This study investigated the prevalence, serotype distribution, virulence gene profiles, and antimicrobial resistance patterns of
L. monocytogenes in ready-to-eat (RTE) food products from Romania. A total of 8151 samples were analyzed, including various processed dairy, bovine, poultry, pork, and fish products. Bacterial isolation was conducted using the classical standard method, followed by confirmation through biochemical and molecular testing. Among the isolated strains, serotypes 1/2a, 1/2b, and 1/2c were identified, with a prevalence of 75% for serotype 1/2a. Additionally, virulence genes specific to listeriolysin O (
hlyA) and regulatory factor A (
prfA) were detected in all isolates. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed varying resistance patterns among the
L. monocytogenes strains. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and oxacillin showed the highest prevalence of resistance at 26.92% and 23.07%, respectively. However, all strains remained susceptible to ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, and moxifloxacin. Notably, 23.07% of the isolates exhibited multidrug resistance, with the most common pattern being resistance to oxacillin, penicillin, and tetracycline. Analysis of antimicrobial resistance genes identified tetracycline resistance genes, particularly
tet(C),
tet(M), and
tet(K), in a significant proportion of isolates. The presence of
ampC and
dfrD genes was also notable, indicating potential mechanisms of resistance. These results emphasize the necessity for ongoing surveillance of
L. monocytogenes in RTE foods and emphasize the importance of thorough monitoring of antimicrobial resistance to guide public health strategies within the European Union.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT