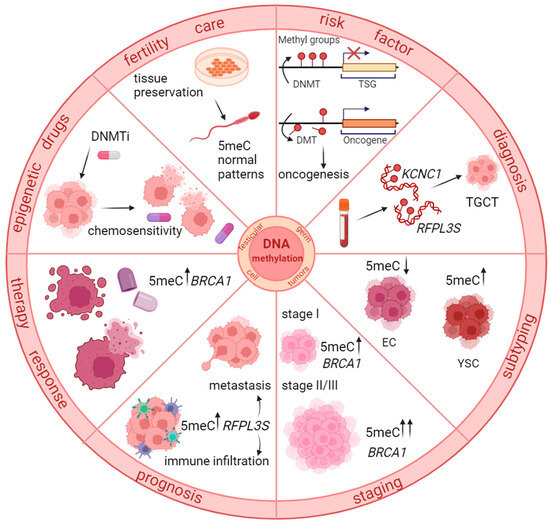
Due to the resistance of Gram-negative bacteria
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to most clinically relevant antimicrobials, the use of traditional antibiotic treatments in hospitals is challenging. The formation of biofilms, which is regulated by the quorum-sensing (QS) system of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA), is an important cause of drug resistance. There are three main QS systems in
P. aeruginosa: the
las system, the
rhl system, and the
pqs system. The inhibitors of the
las system are the most studied. Previously, the compound
AOZ-1 was found to have a certain inhibitory effect on the
las system when screened. In this study, twenty-four compounds were designed and synthesized by modifying the Linker and Rings of
AOZ-1. Using
C. violaceum CV026 as a reporter strain, this study first assessed the inhibitory effects of new compounds against QS, and their SAR was investigated. Then, based on the SAR analysis of compound
AOZ-1 derivatives, the parent core of AOZ-1 was replaced to explore the structural diversity. Then, nine new compounds were designed and synthesized with a new nucleus core component of 3-amino-tetrahydro-l,3-oxazin-2-one. The compound
Y-31 (IC
50 = 91.55 ± 3.35 µM) was found to inhibit the QS of
C. violaceum CV026. Its inhibitory effect on
C. violaceum CV026 was better than that of compound
AOZ-1 (IC
50 > 200 µM). Furthermore, biofilm formation is one of the important causes of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 resistance. In this study, it was found that compound
Y-31, with a new nucleus core component of 3-amino-tetrahydro-l,3-oxazin-2-one, had the highest biofilm inhibition rate (40.44%). The compound
Y-31 has a certain inhibitory effect on the production of PAO1 virulence factors (pyocyanin, rhamnolipid, and elastase) and swarming. When the concentration of compound
Y-31 was 162.5 µM, the inhibition rates of pyocyanin, rhamnolipid, and elastase were 22.48%, 6.13%, and 22.67%, respectively. In vivo, the lifetime of wildtype
Caenorhabditis elegans N2 infected with
P. aeruginosa PAO1 was markedly extended by the new parent nucleus
Y-31. This study also performed cytotoxicity experiments and in vivo pharmacokinetics experiments on the compound
Y-31. In conclusion, this study identified a compound,
Y-31, with a new nucleus core component of 3-amino-tetrahydro-l,3-oxazin-2-one, which is a potential agent for treating
P. aeruginosa PAO1 that is resistant to antibiotics and offers a way to discover novel antibacterial medications.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT