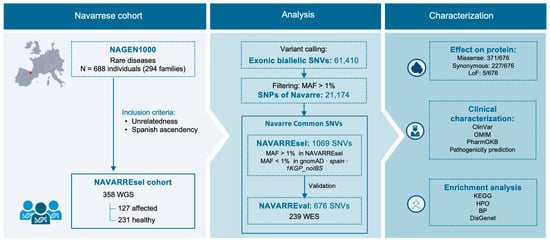
Two samples of Zn
xMn
1−xFe
2O
4 (x = 0, sample A; and x = 0.4, sample B) were synthesized by the hydrothermal method. From complex impedance measurements in the range 100 Hz–2 MHz and for temperatures T between 30 and 130 °C, the barrier energy between localized states ΔE
relax was determined for the first time in these samples. For sample B, a single value of ΔE
relax was highlighted (0.221 eV), whilst, for sample A, two values were obtained (0.012 eV and 0.283 eV, below 85 °C and above 85 °C, respectively), associated with two zones of different conductivities. Using the Mott’s VRH model and the CBH model, we determined for the first time both the bandgap energy barrier (W
m) and the hopping (crossover) frequency (ω
h), at various temperatures. The results show that, for sample A,
Wm has a maximum equal to 0.72 eV at a temperature between 70 and 80 °C, whilst, for sample B, W
m has a minimum equal to 0.28 eV at a temperature of 60 °C, the results being in good agreement with the temperature dependence of the static conductivity σ
DC(T) of the samples. By evaluating σ
DC and eliminating the conduction losses, we identified, using a novel approach, a dielectric relaxation phenomenon in the samples, characterized by the activation energy
EA,rel. At various temperatures, we determined
EA,rel, which ranged from 0.195 eV to 0.77 eV. These results are important, as understanding these electrical properties is crucial to various applications, especially in technologies where temperature variation is significant.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT