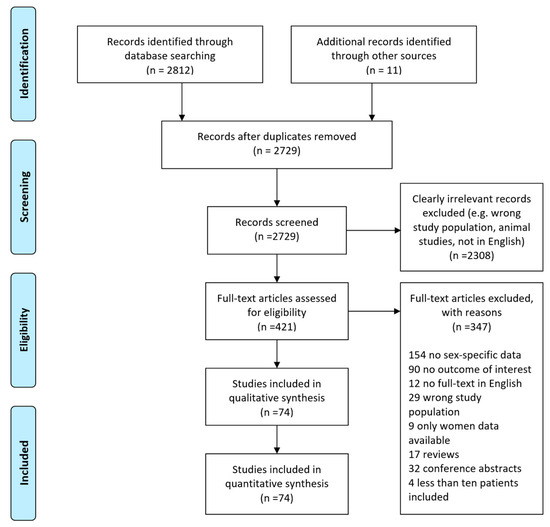
The search for DNA polymorphisms useful for the genetic improvement of dairy farm animals has spanned more than 40 years, yielding relevant findings in cattle for milk traits, where the best combination of alleles for dairy processing has been found in casein genes and in
DGAT1. Nowadays, similar results have not yet been reached in river buffaloes, despite the availability of advanced genomic technologies and accurate phenotype records. The aim of the present study was to investigate and validate the effect of four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in the
CSN1S1,
CSN3,
SCD and
LPL genes on seven milk traits in a larger buffalo population. These SNPs have previously been reported to be associated with, or affect, dairy traits in smaller populations often belonging to one farm. A total of 800 buffaloes were genotyped. The following traits were individually recorded, monthly, throughout each whole lactation period from 2010 to 2021: daily milk yield (dMY, kg), protein yield (dPY, kg) and fat yield (dFY, kg), fat and protein contents (dFP, % and dPP, %), somatic cell count (SCC, 10
3 cell/mL) and urea (mg/dL). A total of 15,742 individual milk test day records (2496 lactations) were available for 680 buffalo cows, with 3.6 ± 1.7 parities (from 1 to 13) and an average of 6.1 ± 1.2 test day records per lactation. Three out four SNPs in the
CSN1S1,
CSN3 and
LPL genes were associated with at least one of analyzed traits. In particular, the
CSN1S1 (AJ005430:c.578C>T) gave favorable associations with all yield traits (dMY,
p = 0.022; dPY,
p = 0.014; dFY,
p = 0.029) and somatic cell score (SCS,
p = 0.032). The
CSN3 (HQ677596: c.536C>T) was positively associated with SCS (
p = 0.005) and milk urea (
p = 0.04). Favorable effects on daily milk yield (dMY,
p = 0.028), fat (dFP,
p = 0.027) and protein (dPP,
p = 0.050) percentages were observed for the
LPL. Conversely, the
SCD did not show any association with milk traits. This is the first example of a confirmation study carried out in the Mediterranean river buffalo for genes of economic interest in the dairy field, and it represents a very important indication for the preselection of young bulls destined for breeding programs aimed at more sustainable dairy production.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT