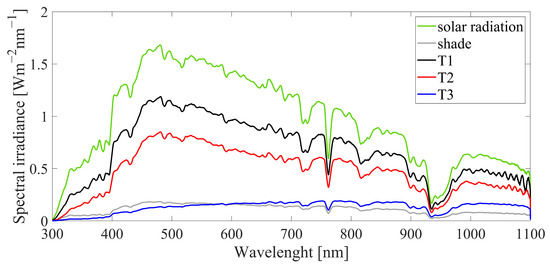
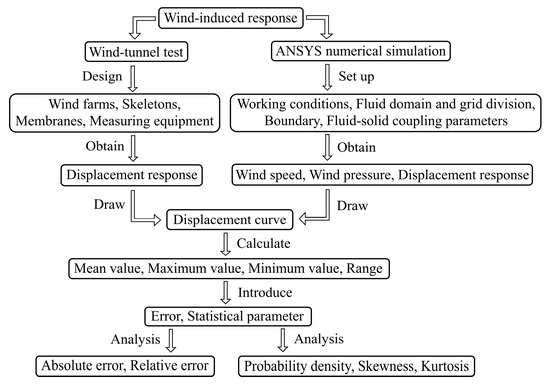
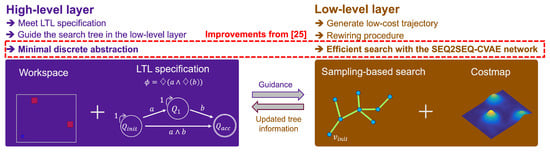
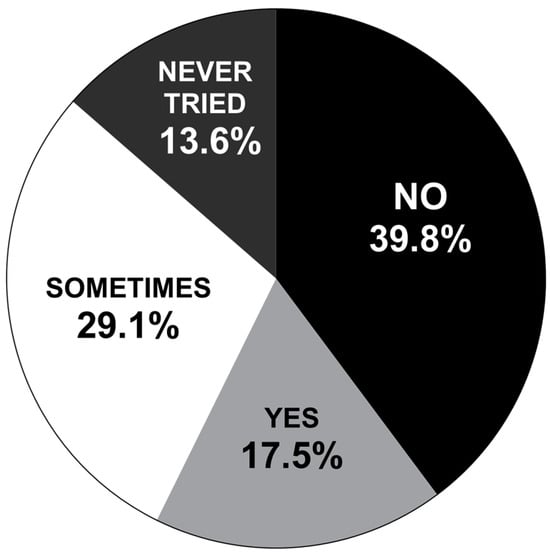
The management and improvement of yam productivity are associated with a good supply of essential nutrients for the growth and development of the crop that has economic viability. This research aimed to evaluate the economic feasibility of foliar fertilization with Zintrac
® in two yam agricultural seasons (2022/2023 and 2023/2024). Therefore, two experiments were conducted at the Rafael Fernandes Experimental Farm, Mossoró, RN, Brazil. The experimental design was in a Latin square design with five treatments of doses of Zintrac
® (0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 L ha
−1) and five replications. Among the production costs of yams, labor and seed acquisition were the most significant. The highest profitability index was achieved with the dose of 1L Zintrac
® ha
−1 in the first season and second season, which corresponded to 78.97 and 57.86%. For the first season, increments were observed in all treatments that received zinc doses with increases of 48.70, 31.22, 14.30, and 15.93% for 1, 2, 3, and 4 L of Zintrac
® ha
−1 compared to the dose of 0 L ha
−1. On the other hand, in the second season, there was an increase only in the dose of 1 L ha
−1 of Zintrac
®, which corresponded to 51.3% in the net yield (ha
−1) of the dose of 0 L ha
−1. Therefore, foliar zinc oxide fertilization was economically viable for the yam crop, obtaining higher economic indices at the dose of 1 L ha
−1. The highest cost for growing yams is using a dose of 4 L ha
−1 of Zintrac
®, totaling USD 6977.59 (first season) and USD 6868.33 (second season)
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT