Open AccessArticle
Impact of Photosynthetic Efficiency on Watermelon Cultivation in the Face of Drought
by
Dayane Mércia Ribeiro Silva, Allan Cunha Barros, Ricardo Barros Silva, Wesley de Oliveira Galdino, José Wilker Germano de Souza, Isabelly Cristina da Silva Marques, Jadielson Inácio de Sousa, Viviane da Silva Lira, Alan Fontes Melo, Lucas da Silva de Abreu, Elias de Oliveira Albuquerque Júnior, Luana do Nascimento Silva Barbosa, Antônio Lucrécio dos Santos Neto, Valdevan Rosendo dos Santos, Francisco Gilvan Borges Ferreira Freitas Júnior, Fernanda Nery Vargens, João Henrique Silva da Luz, Elizabeth Orika Ono and João Domingos Rodrigues
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 950; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050950 (registering DOI) - 01 May 2024
Abstract
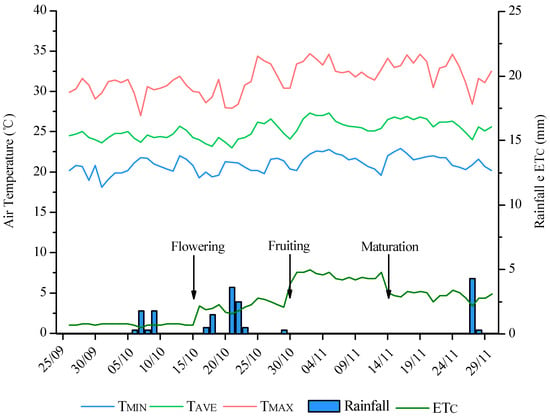
Water availability is a limiting factor for plant production, especially in Brazilian semi-arid regions. The main aim of the study was to investigate the physiological effects of drought during the fruiting stage of watermelon cultivation. A completely randomized block design with four replications
[...] Read more.
Water availability is a limiting factor for plant production, especially in Brazilian semi-arid regions. The main aim of the study was to investigate the physiological effects of drought during the fruiting stage of watermelon cultivation. A completely randomized block design with four replications and six treatments varied by the number of lateral drip tapes (1 or 2) and the duration of drought stress (0, 4, and 8 days) was used. The following parameters were evaluated: relative chlorophyll content, relative leaf water content, electrolyte leakage, CO
2 assimilation (
A), stomatal conductance (
gs), internal CO
2 concentration, leaf temperature, transpiration (
E), water use efficiency (WUE), carboxylation efficiency (CE), yield, thickness, diameter, length, and fruit °brix, at 4 and 8 days of drought. Drought negatively affected photosynthesis, particularly in treatments with a single dripper and 4 days of drought, resulting in reductions of up to 60% in
A, 68% in
gs, 44% in
E, 58% in WUE, and 59% in CE, but did not have a significant effect on watermelon yield after 4 or 8 days of irrigation. It was concluded that drought influences the physiological responses of watermelon plants, mainly in reducing photosynthesis, but does not drastically affect fruit productivity in short periods of stress.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT