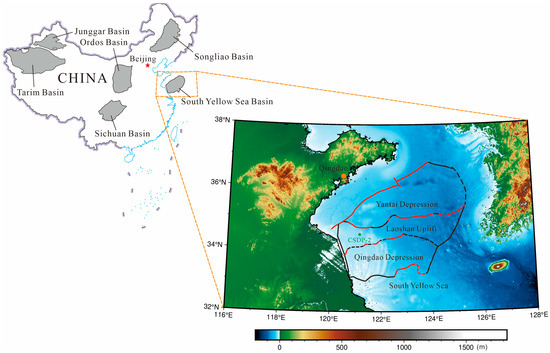
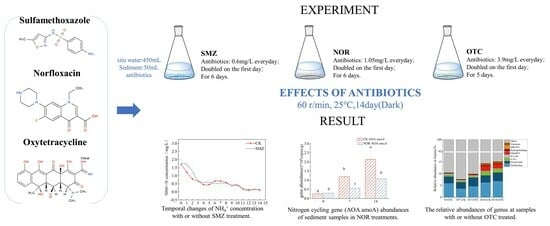
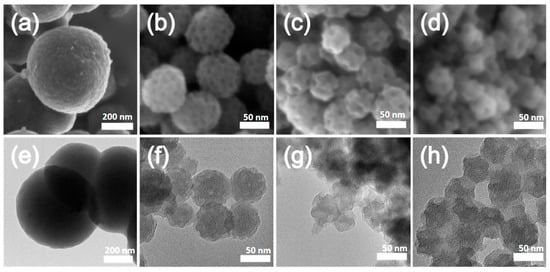
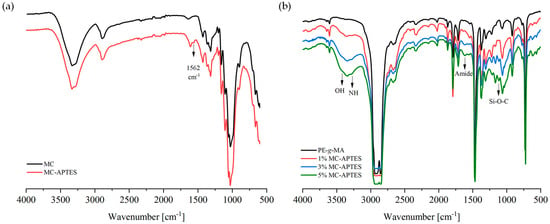
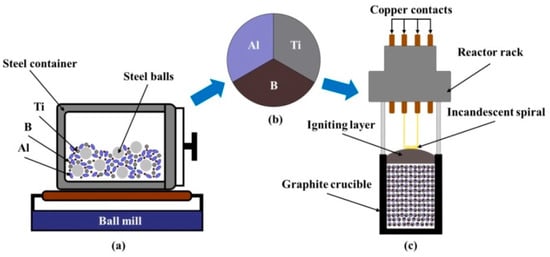
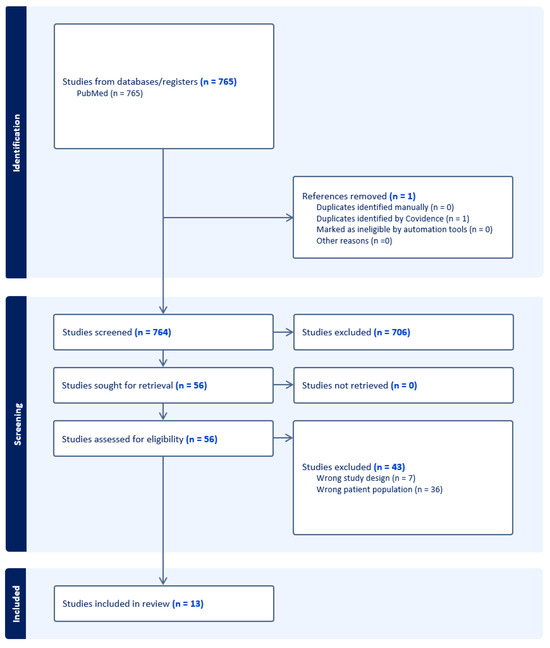
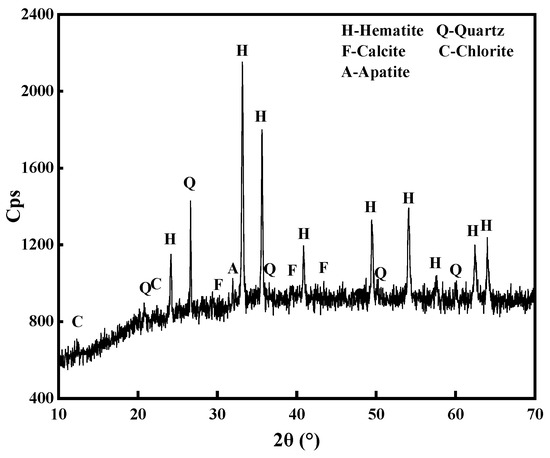
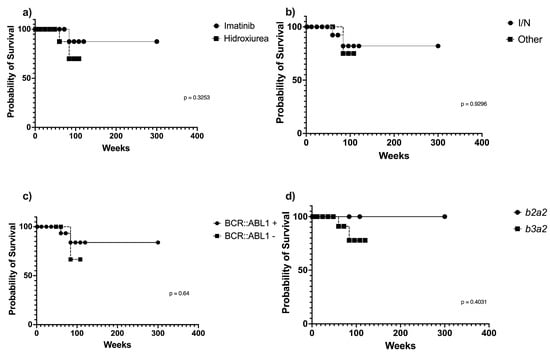
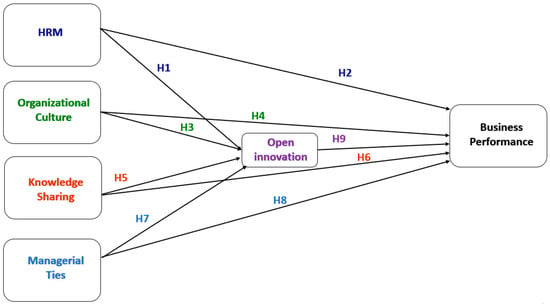
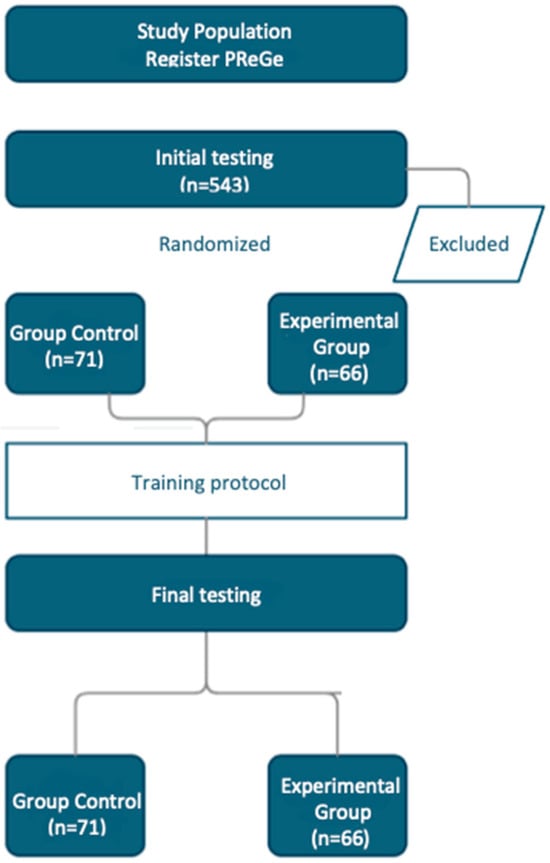
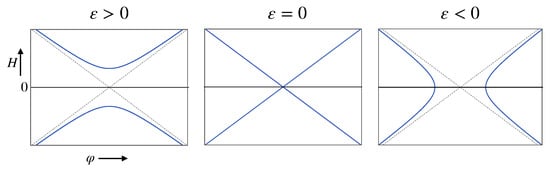
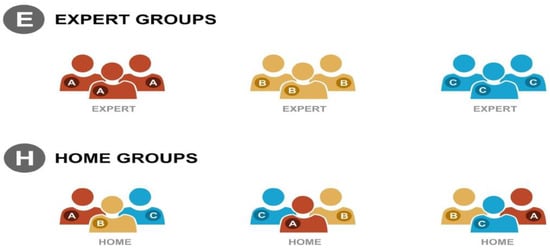
This article attempts to answer the following question: why did the author of the apocryphon called
1 Apocryphal Apocalypse of John choose to efface himself and adopt John as his pseudonym? Why not Peter or Paul? This paper argues that the author of
1 Apocryphal Apocalypse of John intended to harness the audience attached to John, the seer of Revelation, by taking his name as a pseudonym. This paper sustains this claim by demonstrating that, in antiquity, each author had a specific pool of readers, often made out of friends and accolades of the author. Thus, authors’ names evoke an audience attached to them. When an author takes another person’s name to write under, he does so out of necessity, because he does not have an audience. But, when he takes another’s person name, he does so hoping to trick the audience of the impersonated into reading him. Based on this insight, this article concludes that the author of
1 Apocr. Apoc. John wanted the readers of canonical Revelation to engage with his work and that he achieved his purpose as evinced by the fact that the titles of both works share an uncanny resemblance, ranging from identical titles to similar wording. Since titles in antiquity were given to the works by their readers, the most logical explanation for canonical Revelation and
1 Apocr. Apoc. John having the same titles is that they both shared the same readers. Finally, this article argues that, in line with recent research on the use of pseudepigraphy in Jewish, Christian, and Roman contexts, the author of
1 Apocr. Apoc. John wanted to be read by CR’s readers because he wanted to expand, criticize, rework, and update CR’s eschatological discourse, exemplified by a close reading of how
1 Apocr. Apoc. John criticized, reworked, and updated CR’s presentation of the resurrection to bring it in harmony with late Christian reflection on the subject.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT