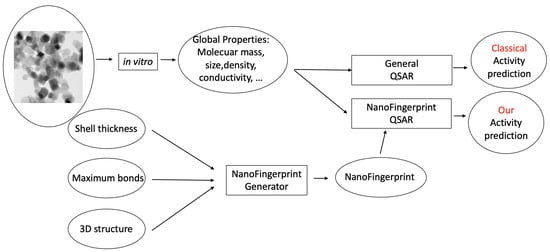
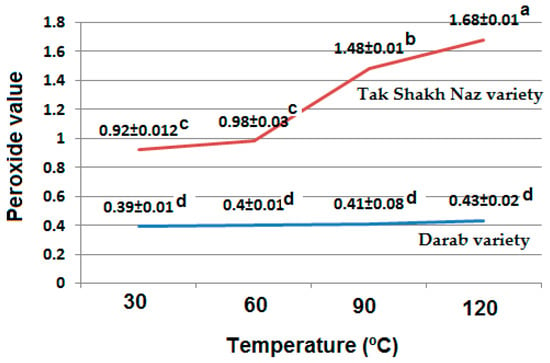
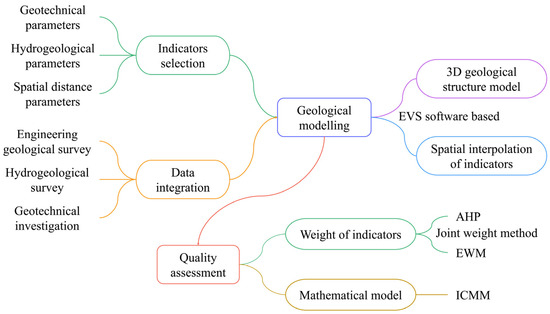
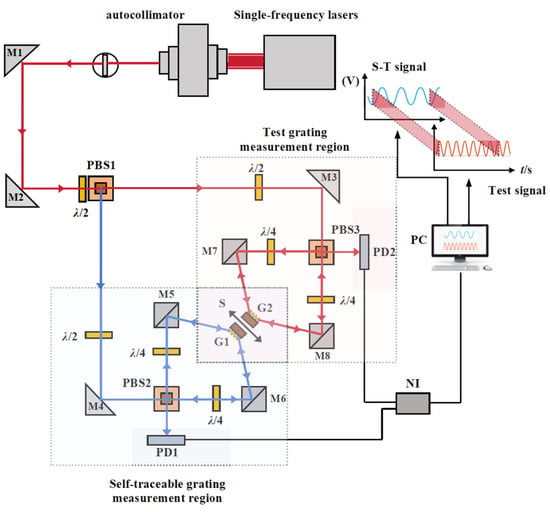
Hyperlipidemia, characterized by elevated cholesterol, lipids, and triglycerides in the bloodstream, is linked to hepatic oxidative damage.
Doenjang, a traditional Korean condiment made from fermented soybeans, is known for its health benefits, yet its anti-hyperlipidemic effects remain understudied. Our study aimed to
[...] Read more.
Hyperlipidemia, characterized by elevated cholesterol, lipids, and triglycerides in the bloodstream, is linked to hepatic oxidative damage.
Doenjang, a traditional Korean condiment made from fermented soybeans, is known for its health benefits, yet its anti-hyperlipidemic effects remain understudied. Our study aimed to assess the hypolipidemic and hepatic protective effects of
Doenjang on male ICR mice fed a high-fat cholesterol diet for 8 weeks. Mice were divided into three groups: the normal diet (ND), the high-fat cholesterol diet (HD), and the
Doenjang-supplemented HD diet (DS) group.
Doenjang supplementation significantly regulated total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and HDL cholesterol levels compared to the HD group. It also downregulated lipogenic genes, including PPARγ, FAS, and ACC, and positively influenced the cholesterol metabolism-related genes HMGCR and LXR. Moreover,
Doenjang intake increased serum glutathione levels, activated oxidative stress defense genes (NRF2, SOD, GPx1, and CAT), positively modulated inflammation genes (NF-kB and IL6) in hepatic tissue, and reduced malondialdehyde levels. Our findings highlight the effectiveness of traditional
Doenjang in preventing diet-induced hyperlipidemia and protecting against hepatic oxidative damage.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT