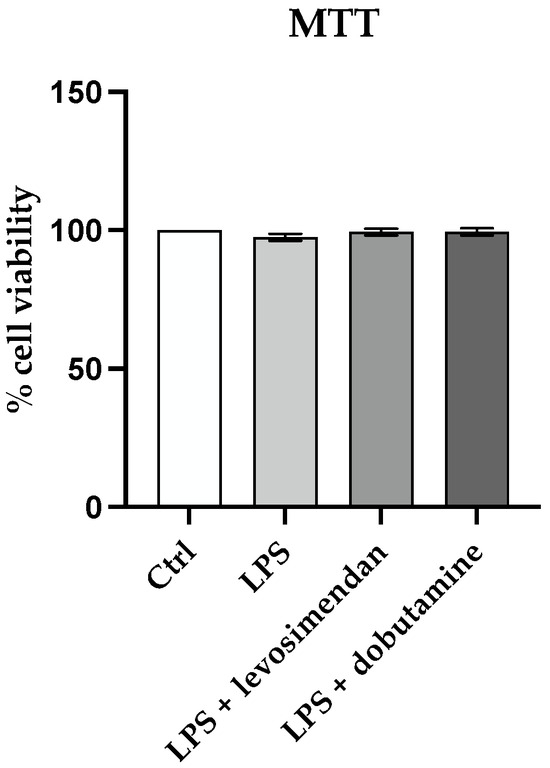
Airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) is a protective mechanical ventilation mode for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) that theoretically may reduce ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) and ARDS-related mortality. However, there is no standard method to set and adjust the APRV mode shown to be optimal. Therefore, we performed a meta-regression analysis to evaluate how the four individual APRV settings impacted the outcome in these patients.
Methods: Studies investigating the use of the APRV mode for ARDS patients were searched from electronic databases. We tested individual settings, including (1) high airway pressure (P
High); (2) low airway pressure (P
Low); (3) time at high airway pressure (T
High); and (4) time at low pressure (T
Low) for association with PaO
2/FiO
2 ratio and ICU length of stay.
Results: There was no significant difference in PaO
2/FiO
2 ratio between the groups in any of the four settings (P
High difference −12.0 [95% CI −100.4, 86.4]; P
Low difference 54.3 [95% CI −52.6, 161.1]; T
Low difference −27.19 [95% CI −127.0, 72.6]; T
High difference −51.4 [95% CI −170.3, 67.5]). There was high heterogeneity across all parameters (P
hHgh I
2 = 99.46%, P
Low I
2 = 99.16%, T
Low I
2 = 99.31%, T
High I
2 = 99.29%).
Conclusions: None of the four individual APRV settings independently were associated with differences in outcome. A holistic approach, analyzing all settings in combination, may improve APRV efficacy since it is known that small differences in ventilator settings can significantly alter mortality. Future clinical trials should set and adjust APRV based on the best current scientific evidence available.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT