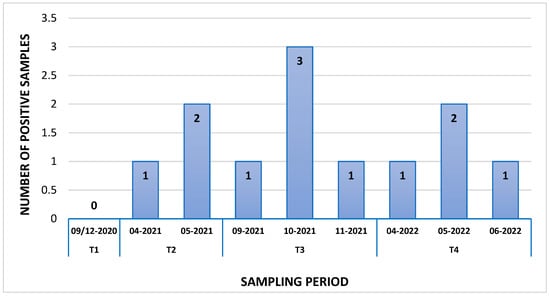
Scorpion envenomation poses a global public health issue, with an estimated 1,500,000 cases worldwide annually resulting in 2600 deaths. North Africa, particularly Morocco, experiences severe envenomations, mainly attributed to
Androctonus mauretanicus and
Buthus occitanus in Morocco, and
Buthus occitanus and
Androctonus australis hector
[...] Read more.
Scorpion envenomation poses a global public health issue, with an estimated 1,500,000 cases worldwide annually resulting in 2600 deaths. North Africa, particularly Morocco, experiences severe envenomations, mainly attributed to
Androctonus mauretanicus and
Buthus occitanus in Morocco, and
Buthus occitanus and
Androctonus australis hector in Algeria and Tunisia, with case numbers often underestimated. Current treatment relies mainly on symptomatic approaches, except in Morocco, where management is limited to symptomatic treatment due to controversies regarding specific treatment. In Morocco, between 30,000 and 50,000 scorpion envenomation cases are reported annually, leading to hundreds of deaths, mainly among children. Controversies among clinicians persist regarding the appropriate course of action, often limiting treatments to symptomatic measures. The absence of a specific antivenom for the venoms of the most lethal scorpions further exacerbates the situation. This study aims to address this gap by developing a monovalent antivenom against the endemic and most dangerous scorpion,
Androctonus mauretanicus. The antivenom was produced by immunizing albino rabbits with a mixture of
Androctonus mauretanicus venom collected from high-risk areas in Morocco. Immunizations were performed by subcutaneous injections at multiple sites near the lymphatic system, following an immunization schedule. Production control of neutralizing antibody titers was conducted through immunodiffusion. Once a sufficient antibody titer was achieved, blood collection was performed, and the recovered plasma underwent affinity chromatography. The efficacy of purified IgG was evaluated by determining the ED
50 in mice, complemented by histological and immunohistochemical studies on its ability to neutralize venom-induced tissue alterations and the neutralization of toxins bound to receptors in the studied organs. The monovalent antivenom demonstrated specificity against
Androctonus mauretanicus venom and effective cross-protection against the venom of the scorpions
Buthus occitanus and
Androctonus australis hector, highly implicated in lethal envenomations in the Maghreb. This study shows that the developed monovalent antivenom exhibits notable efficacy against local scorpions and a surprising ability to neutralize the most lethal envenomations in North Africa. These results pave the way for a new, more specific, and promising therapeutic approach to countering severe scorpion envenomations, especially in Morocco, where specific treatment is lacking.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT