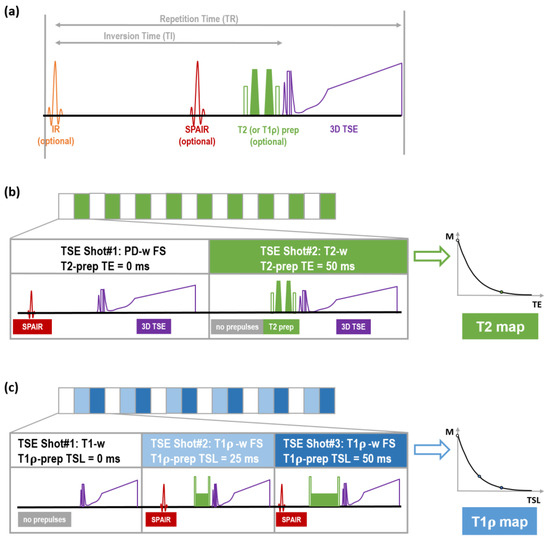
An experiment was carried out to evaluate the effect of spring and autumn seasons on the reproductive activity of Merino Socorro Island ewes and their crosses with Pelibuey under heat stress (
HS) conditions in the tropics. All ewes (
n = 80) were randomly assigned to one of two breeds during the first and second periods, respectively: (1) Twenty Socorro Island Merino ewes (
SIM) and (2) 20 Pelibuey Crossbred ewes (
PBC). Animals were fed the same diet and given water ad libitum. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS statistical software 9.12 procedures. In both seasons, a mean of more than 80 U of maximum THI was obtained, while in spring and autumn, the minimum THI exceeded 30 and 40 U, respectively. All animals were in oestrus and ovulated in both seasons. The frequency of animals in spring during the first 48 h of oestrus expression was greater (
p < 0.05) than 48–55 h but similar (
p > 0.05) than 55–65 h; in autumn during the first 48 h and 48–55 h were similar (
p > 0.05), but different (
p < 0.05) than 55–65 h. The duration of oestrus expression was longer in the spring than in the autumn (
p < 0.05). The frequency of animals was higher (
p < 0.05) in SIM than in PBC ewes during the first oestrus cycle (1–17 d) and was also higher (
p < 0.05) in PBC than in SIM ewes during the second oestrus cycle (18–35 d). The SIM ewes produced more (
p < 0.05) progesterone (
P4) than the PBC ewes. During the sampling days of the oestrus cycle, more P
4 was created in autumn than in spring (
p < 0.05). Both breeds showed severe HS. In the future, ewes treated under assisted reproductive programs in the tropics may improve reproductive efficiency.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT