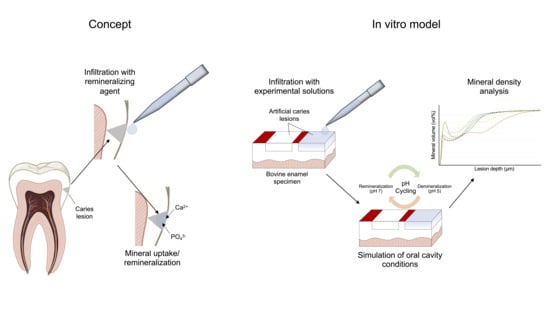
The application of calcium coacervates (CCs) may hold promise for dental hard tissue remineralization. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of the infiltration of artificial enamel lesions with a CC and its single components including polyacrylic acid (PAA) compared to that of the self-assembling peptide P
11-4 in a pH-cycling (pHC) model. Enamel specimens were prepared from bovine incisors, partly varnished, and stored in demineralizing solution (DS; pH 4.95; 17 d) to create two enamel lesions per sample. The specimens were randomly allocated to six groups (n = 15). While one lesion per specimen served as the no-treatment control (NTC), another lesion (treatment, T) was etched (H
3PO
4, 5 s), air-dried and subsequently infiltrated for 10 min with either a CC (10 mg/mL PAA, 50 mM CaCl
2 (Ca) and 1 M K
2HPO
4 (PO
4)) (groups CC and CC + DS) or its components PAA, Ca or PO
4. As a commercial control, the self-assembling peptide P
11-4 (Curodont
TM Repair, Credentis, Switzerland) was tested. The specimens were cut perpendicularly to the lesions, with half serving as the baseline (BL) while the other half was exposed to either a demineralization solution for 20 d (pH 4.95; group CC + DS) or pHC for 28 d (pH 4.95, 3 h; pH 7, 21 h; all five of the other groups). The difference in integrated mineral loss between the lesions at BL and after the DS or pHC, respectively, was analyzed using transversal microradiography (ΔΔZ = ΔZ
pHC − ΔZ
baseline). Compared to the NTC, the mineral gain in the T group was significantly higher in the CC + DS, CC and PAA (
p < 0.05, Wilcoxon). In all of the other groups, no significant differences between treated and untreated lesions were detected (
p > 0.05). Infiltration with the CC and PAA resulted in a consistent mineral gain throughout the lesion body. The CC as well as its component PAA alone promoted the remineralization of artificial caries lesions in the tested pHC model. Infiltration with PAA further resulted in mineral gain in deeper areas of the lesion body.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT