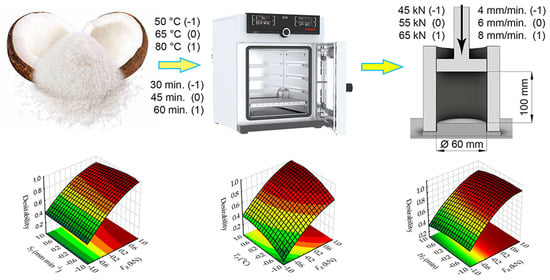
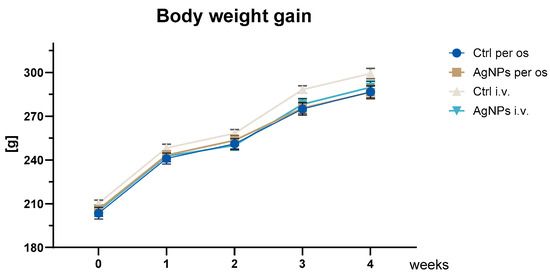
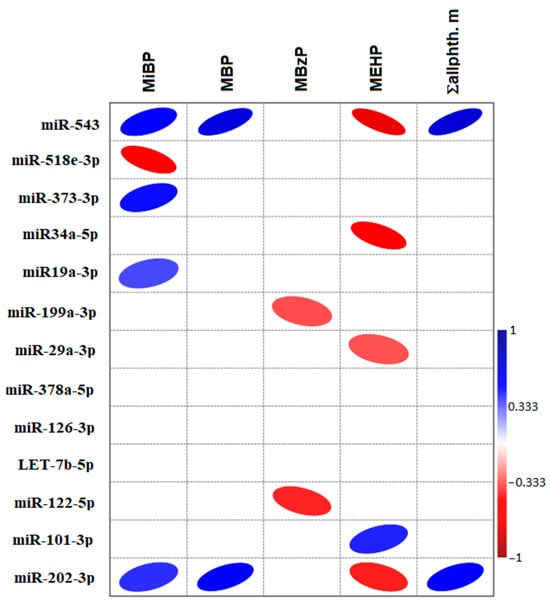
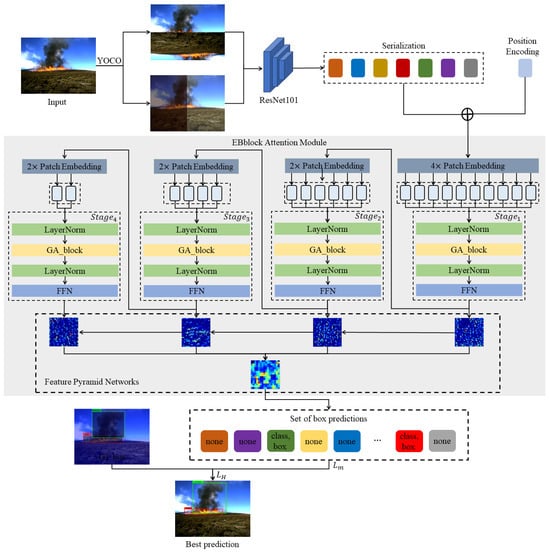
Forest fires represent a significant menace to both the ecological equilibrium of forests and the safety of human life and property. Upon ignition, fires frequently generate billowing smoke. The prompt identification and management of fire sources and smoke can efficiently avert the occurrence of extensive forest fires, thereby safeguarding both forest resources and human well-being. Although drone patrols have emerged as a primary method for forest-fire prevention, the unique characteristics of forest-fire images captured from high altitudes present challenges. These include remote distances, small fire points, smoke targets with light hues, and complex, ever-changing background environments. Consequently, traditional target-detection networks frequently exhibit diminished accuracy when handling such images. In this study, we introduce a cutting-edge drone-based network designed for the detection of forest fires and smoke, named FSNet. To begin, FSNet employs the YOCO data-augmentation method to enhance image processing, thereby augmenting both local and overall diversity within forest-fire images. Next, building upon the transformer framework, we introduce the EBblock attention module. Within this module, we introduce the notion of “groups”, maximizing the utilization of the interplay between patch tokens and groups to compute the attention map. This approach facilitates the extraction of correlations among patch tokens, between patch tokens and groups, and among groups. This approach enables the comprehensive feature extraction of fire points and smoke within the image, minimizing background interference. Across the four stages of the EBblock, we leverage a feature pyramid to integrate the outputs from each stage, thereby mitigating the loss of small target features. Simultaneously, we introduce a tailored loss function, denoted as
, specifically designed for FSNet. This ensures the model’s ability to learn effectively and produce high-quality prediction boxes. We assess the performance of the FSNet model across three publicly available forest-fire datasets, utilizing mAP, Recall, and FPS as evaluation metrics. The outcomes reveal that FSNet achieves remarkable results: on the Flame, Corsican, and D-Fire datasets, it attains mAP scores of 97.2%, 87.5%, and 94.3%, respectively, with Recall rates of 93.9%, 87.3%, and 90.8%, respectively, and FPS values of 91.2, 90.7, and 92.6, respectively. Furthermore, extensive comparative and ablation experiments validate the superior performance of the FSNet model.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT