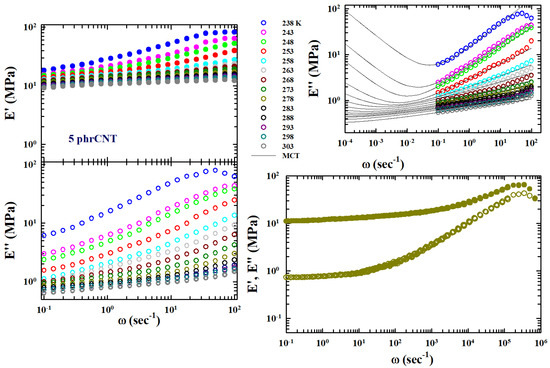
In the dynamic field of radiopharmaceuticals, innovating targeted agents for cancer diagnosis and therapy is crucial. Our study enriches this evolving landscape by evaluating the potential of radioiodinated anastrozole ([
125I]anastrozole) and radioiodinated epirubicin ([
125I]epirubicin) as targeting agents against MTHFD2-driven
[...] Read more.
In the dynamic field of radiopharmaceuticals, innovating targeted agents for cancer diagnosis and therapy is crucial. Our study enriches this evolving landscape by evaluating the potential of radioiodinated anastrozole ([
125I]anastrozole) and radioiodinated epirubicin ([
125I]epirubicin) as targeting agents against MTHFD2-driven tumors. MTHFD2, which is pivotal in one-carbon metabolism, is notably upregulated in various cancers, presenting a novel target for radiopharmaceutical application. Through molecular docking and 200 ns molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, we assess the binding efficiency and stability of [
125I]anastrozole and [
125I]epirubicin with MTHFD2. Molecular docking illustrates that [
125I]epirubicin has a superior binding free energy (∆
Gbind) of −41.25 kJ/mol compared to −39.07 kJ/mol for [
125I]anastrozole and −38.53 kJ/mol for the control ligand, suggesting that it has a higher affinity for MTHFD2. MD simulations reinforce this, showing stable binding, as evidenced by root mean square deviation (RMSD) values within a narrow range, underscoring the structural integrity of the enzyme–ligand complexes. The root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) analysis indicates consistent dynamic behavior of the MTHFD2 complex upon binding with [
125I]anastrozole and [
125I]epirubicin akin to the control. The radius of gyration (RG) measurements of 16.90 Å for MTHFD2-[
125I]anastrozole and 16.84 Å for MTHFD2-[
125I]epirubicin confirm minimal structural disruption upon binding. The hydrogen bond analysis reveals averages of two and three stable hydrogen bonds for [
125I]anastrozole and [
125I]epirubicin complexes, respectively, highlighting crucial stabilizing interactions. The MM-PBSA calculations further endorse the thermodynamic favorability of these interactions, with binding free energies of −48.49 ± 0.11 kJ/mol for [
125I]anastrozole and −43.8 kJ/mol for MTHFD2-. The significant contribution of Van der Waals and electrostatic interactions to the binding affinities of [
125I]anastrozole and [
125I]epirubicin, respectively, underscores their potential efficacy for targeted tumor imaging and therapy. These computational findings lay the groundwork for the future experimental validation of [
125I]anastrozole and [
125I]epirubicin as MTHFD2 inhibitors, heralding a notable advancement in precision oncology tools. The data necessitate subsequent in vitro and in vivo assays to corroborate these results.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT