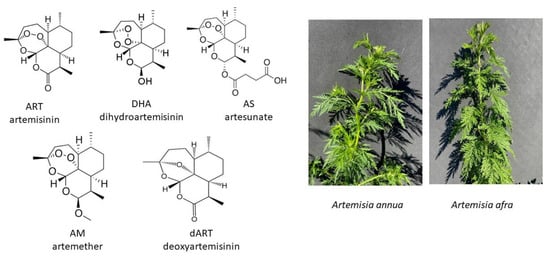
Fibrosis is a ubiquitous pathology, and prior studies have indicated that various artemisinin (ART) derivatives (including artesunate (AS), artemether (AM), and dihydroartemisinin (DHA)) can reduce fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. The medicinal plant
Artemisia annua L. is the natural source of ART and is widely used, especially in underdeveloped countries, to treat a variety of diseases including malaria.
A. afra contains no ART but is also antimalarial. Using human dermal fibroblasts (CRL-2097), we compared the effects of
A. annua and
A. afra tea infusions, ART, AS, AM, DHA, and a liver metabolite of ART, deoxyART (dART), on fibroblast viability and expression of key fibrotic marker genes after 1 and 4 days of treatment. AS, DHA, and
Artemisia teas reduced fibroblast viability 4 d post-treatment in up to 80% of their respective controls. After 4 d of treatment, AS DHA and
Artemisia teas downregulated
ACTA2 up to 10 fold while ART had no significant effect, and AM increased viability by 10%.
MMP1 and
MMP3 were upregulated by AS, 17.5 and 32.6 fold, respectively, and by DHA, 8 and 51.8 fold, respectively. ART had no effect, but
A. annua and
A. afra teas increased
MMP3 5 and 16-fold, respectively. Although
A. afra tea increased
COL3A1 5 fold,
MMP1 decreased >7 fold with no change in either transcript by
A. annua tea. Although
A. annua contains ART, it had a significantly greater anti-fibrotic effect than ART alone but was less effective than
A. afra. Immunofluorescent staining for smooth-muscle α-actin (α-SMA) correlated well with the transcriptional responses of drug-treated fibroblasts. Together, proliferation, qPCR, and immunofluorescence results show that treatment with ART, AS, DHA, and the two
Artemisia teas yield differing responses, including those related to fibrosis, in human dermal fibroblasts, with evidence also of remodeling of fibrotic ECM.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT