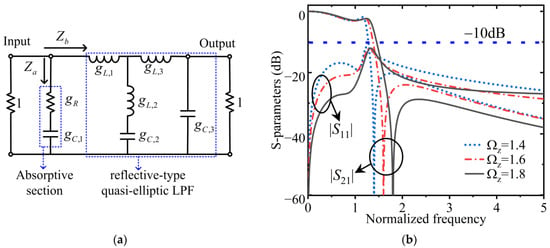
Alternanthera philoxeroides and
Hypophthalmichthys molitrix offer significant nutritional benefits. This study evaluates the proximate composition, amino acid profile, GC-MS analysis, FT-IR spectroscopy, SEM and EDX, and color values of edible paper sheets (EPSs) derived from
Alternanthera philoxeroides incorporating different levels of
Hypophthalmichthys molitrix
[...] Read more.
Alternanthera philoxeroides and
Hypophthalmichthys molitrix offer significant nutritional benefits. This study evaluates the proximate composition, amino acid profile, GC-MS analysis, FT-IR spectroscopy, SEM and EDX, and color values of edible paper sheets (EPSs) derived from
Alternanthera philoxeroides incorporating different levels of
Hypophthalmichthys molitrix flesh. The protein content in the EPSs varied based on fish flesh incorporation, peaking at 52.66% in Ap100/Hm300 (Non-boil). Protein and carbohydrate contents showed an inverse correlation across EPSs, with the highest carbohydrate content of 60.89% in sample Ap400/Hm0 (Boil). Lipid content was also found to correlate with
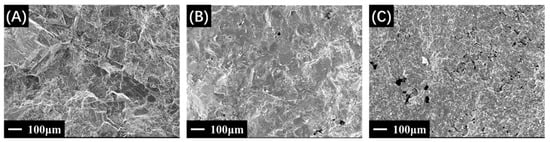
H. molitrix flesh content in EPSs, ranging from 1.59% to 18.41%. Amino acid analysis identified 11 types, with methionine as the most prevalent, followed by leucine, phenylalanine, and lysine. GC-MS analysis revealed 51 bioactive compounds, including carbonic acid, hentriacontane, and various fatty acids. FT-IR analysis showed characteristic bonds, while color analysis displayed L* values ranging from 24.37 to 30.97. SEM analyses depicted the microstructure, surface view, and elemental composition of the EPSs, and EDX showed an abundance of Ca, N, K, O, C, Mg, Na, P, Cl, Mn, and Fe. Therefore, EPSs prepared from
A. philoxeroides and
H. molitrix could offer a promising approach for effectively utilizing aquatic biomass and providing both plant and animal nutrients to consumers.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT