Remote sensing technologies are critical for analyzing the escalating impacts of global climate change and increasing urbanization, providing vital insights into land surface temperature (LST), land use and cover (LULC) changes, and the identification of urban heat island (UHI) and surface urban heat
[...] Read more.
Remote sensing technologies are critical for analyzing the escalating impacts of global climate change and increasing urbanization, providing vital insights into land surface temperature (LST), land use and cover (LULC) changes, and the identification of urban heat island (UHI) and surface urban heat island (SUHI) phenomena. This research focuses on the nexus between LULC alterations and variations in LST and air temperature (T
air), with a specific emphasis on the intensified SUHI effect in Kharkiv, Ukraine. Employing an integrated approach, this study analyzes time-series data from Landsat and MODIS satellites, alongside T
air climate records, utilizing machine learning techniques and linear regression analysis. Key findings indicate a statistically significant upward trend in T
air and LST during the summer months from 1984 to 2023, with a notable positive correlation between T
air and LST across both datasets. MODIS data exhibit a stronger correlation (R
2 = 0.879) compared to Landsat (R
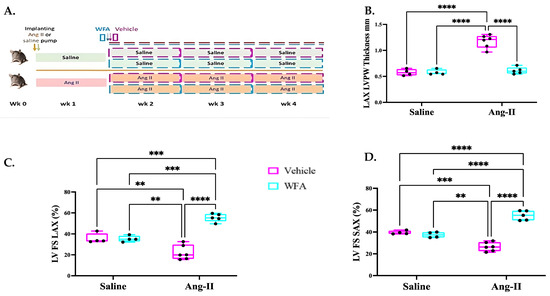
2 = 0.663). The application of a supervised classification through Random Forest algorithms and vegetation indices on LULC data reveals significant alterations: a 70.3% increase in urban land and a decrement in vegetative cover comprising a 15.5% reduction in dense vegetation and a 62.9% decrease in sparse vegetation. Change detection analysis elucidates a 24.6% conversion of sparse vegetation into urban land, underscoring a pronounced trajectory towards urbanization. Temporal and seasonal LST variations across different LULC classes were analyzed using kernel density estimation (KDE) and boxplot analysis. Urban areas and sparse vegetation had the smallest average LST fluctuations, at 2.09 °C and 2.16 °C, respectively, but recorded the most extreme LST values. Water and dense vegetation classes exhibited slightly larger fluctuations of 2.30 °C and 2.24 °C, with the bare land class showing the highest fluctuation 2.46 °C, but fewer extremes. Quantitative analysis with the application of Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests across various LULC classes substantiated the normality of LST distributions
p > 0.05 for both monthly and annual datasets. Conversely, the Shapiro-Wilk test validated the normal distribution hypothesis exclusively for monthly data, indicating deviations from normality in the annual data. Thresholded LST classifies urban and bare lands as the warmest classes at 39.51 °C and 38.20 °C, respectively, and classifies water at 35.96 °C, dense vegetation at 35.52 °C, and sparse vegetation 37.71 °C as the coldest, which is a trend that is consistent annually and monthly. The analysis of SUHI effects demonstrates an increasing trend in UHI intensity, with statistical trends indicating a growth in average SUHI values over time. This comprehensive study underscores the critical role of remote sensing in understanding and addressing the impacts of climate change and urbanization on local and global climates, emphasizing the need for sustainable urban planning and green infrastructure to mitigate UHI effects.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT