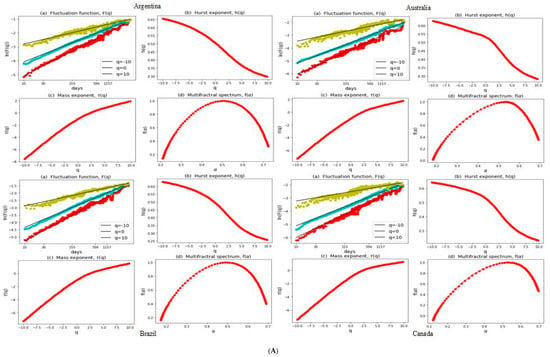
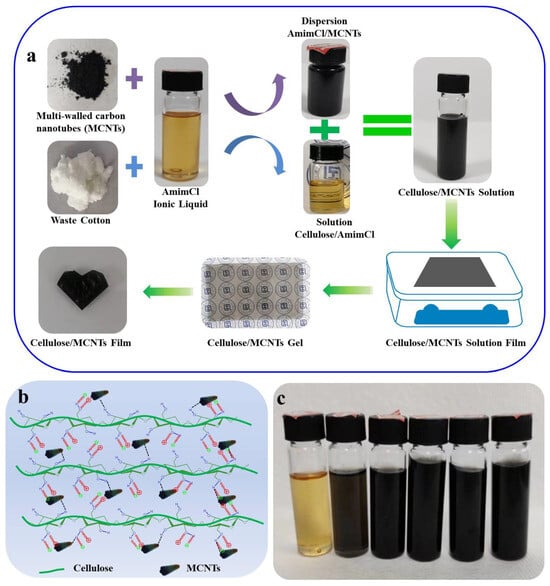
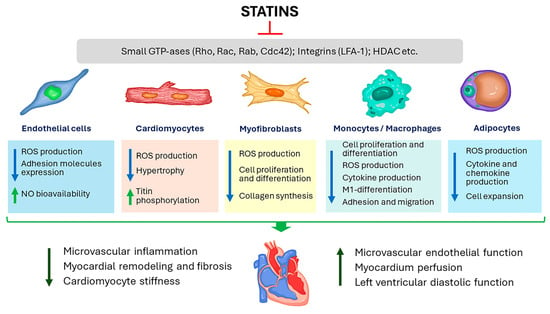
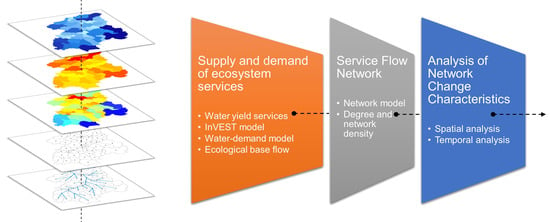
The presence of enteric pathogens in produce can serve as a significant means of transmitting infections to consumers. Notably, tomatoes, as a type of produce, have been implicated in outbreaks caused by various human pathogens, such as
Salmonella enterica and pathogenic
Escherichia coli.
[...] Read more.
The presence of enteric pathogens in produce can serve as a significant means of transmitting infections to consumers. Notably, tomatoes, as a type of produce, have been implicated in outbreaks caused by various human pathogens, such as
Salmonella enterica and pathogenic
Escherichia coli. However, the survival characteristics of
Shigella spp. in tomatoes have not been thoroughly investigated. In this study, we assess the survival of
S. flexneri 2a in two distinct varieties of post-harvested tomatoes.
S. flexneri 2a was used to inoculate both regular-sized Vine tomatoes and cherry-type Mini Plum tomatoes. Our findings reveal no significant difference in
Shigella survival in the pericarp of both varieties on day 2 post-inoculation. However, a significant disparity emerges on day 6, where all recovered
Shigella colonies exclusively belong to the Mini Plum variety, with none associated with the Vine type. When
Shigella was inoculated into the locular cavity (deep inoculation), no significant difference between varieties was observed. Additionally, we investigate the potential role of the SRL pathogenicity island (SRL PAI) in the survival and fitness of
S. flexneri 2a in post-harvested tomatoes. Our results indicate that while the SRL PAI is not linked to the survival of the strains in tomato, it does impact their fitness. These findings underscore the variability in
Shigella strains’ survival capabilities depending on the tomato variety, highlighting the importance of understanding
Shigella ecology beyond the human host and identifying molecular determinants influencing bacterial survival to mitigate the risk of future outbreaks. The significance of this data on
Shigella persistence in fresh vegetables should not be underestimated, as even a small number of
Shigella cells can pose a threat to the health of individuals.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT