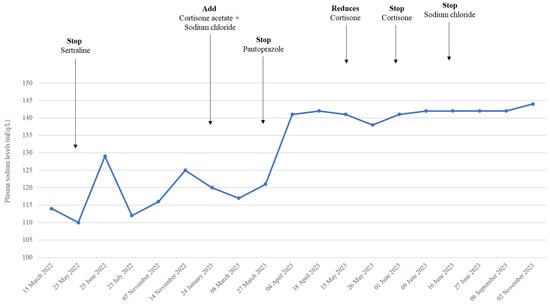
Lumbar lordotic curvature (LLC), closely associated with low back pain (LBP) when decreased, is infrequently assessed in clinical settings due to the spatiotemporal limitations of radiographic methods. To overcome these constraints, this study used an inertial measurement system to compare the magnitude and
[...] Read more.
Lumbar lordotic curvature (LLC), closely associated with low back pain (LBP) when decreased, is infrequently assessed in clinical settings due to the spatiotemporal limitations of radiographic methods. To overcome these constraints, this study used an inertial measurement system to compare the magnitude and maintenance of LLC across various sitting conditions, categorized into three aspects: verbal instructions, chair type, and desk task types.
Methods: Twenty-nine healthy participants were instructed to sit for 3 min with two wireless sensors placed on the 12th thoracic vertebra and the 2nd sacral vertebra. The lumbar lordotic angle (LLA) was measured using relative angles for the mediolateral axis and comparisons were made within each sitting category.
Results: The maintenance of LLA (
LLAdev) was significantly smaller when participants were instructed to sit upright (−3.7 ± 3.9°) compared to that of their habitual sitting posture (−1.2 ± 2.4°) (
p = 0.001), while the magnitude of LLA (
LLAavg) was significantly larger with an upright sitting posture (
p = 0.001).
LLAdev was significantly larger when using an office chair (−0.4 ± 1.1°) than when using a stool (−3.2 ± 7.1°) (
p = 0.033), and
LLAavg was also significantly larger with the office chair (
p < 0.001). Among the desk tasks,
LLAavg was largest during keyboard tasks (
p < 0.001), followed by mouse and writing tasks;
LLAdev showed a similar trend without statistical significance (keyboard, −1.2 ± 3.0°; mouse, −1.8 ± 2.2°; writing, −2.9 ± 3.1°) (
p = 0.067).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that strategies including the use of an office chair and preference for computer work may help preserve LLC, whereas in the case of cueing, repetition may be necessary.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT