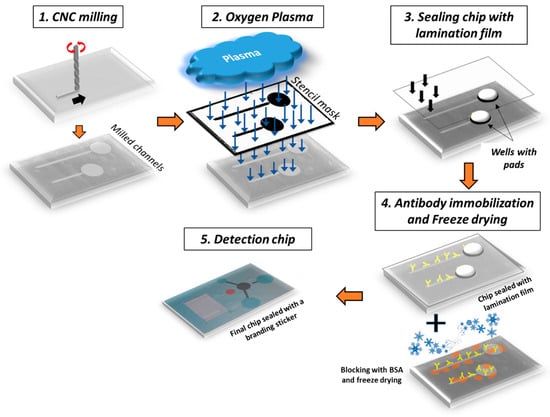
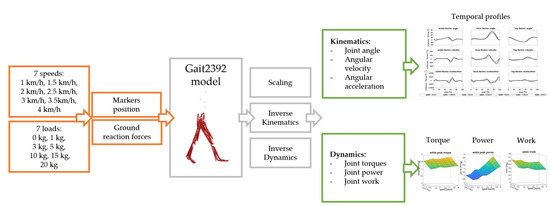
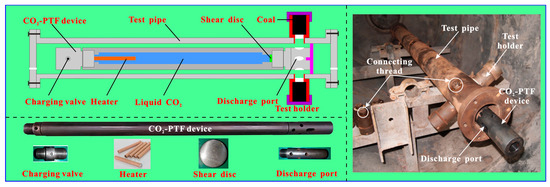
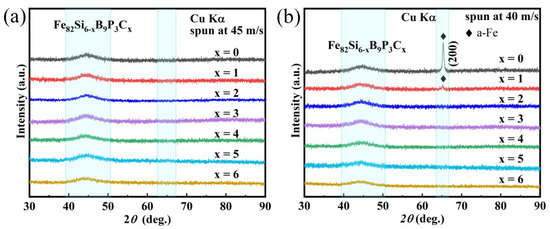
To compare the environmental space of four
Anastrepha species in different ENSO episodes (El Niño, El Neutro and La Niña), we built ecological niche models with NicheA software. We analysed the fundamental niche and the combined establishment risk maps of these species developed
[...] Read more.
To compare the environmental space of four
Anastrepha species in different ENSO episodes (El Niño, El Neutro and La Niña), we built ecological niche models with NicheA software. We analysed the fundamental niche and the combined establishment risk maps of these species developed with the ArcGisPro combine geoprocess. A comparison of the ellipsoids that represent the fundamental niche existing for the species showed changes in the El Niño, El Neutro and La Niña episodes. For
A. grandis in the El Niño vs. El Neutro episodes, there was a Jaccard index of 0.3841, while the comparison between the La Niña vs. El Neutro episodes presented a Jaccard index of 0.6192.
A. serpentina in the El Niño vs. El Neutro and La Niña vs. El Neutro episodes presented Jaccard indices of 0.3281 and 0.6328, respectively. For
A. obliqua, the comparison between the El Niño vs. El Neutro and La Niña vs. El Neutro episodes presented Jaccard indices of 0.3518 and 0.7472, respectively. For
A. striata, comparisons between the episodes of El Niño vs. El Neutro and La Niña vs. El Neutro presented Jaccard indices of 0.3325 and 0.6022, respectively. When studying the comparison between Anastrepha species and the different ENSO climatic episodes, we found that in the El Niño episode, the comparisons with the best environmental similarity were
A. obliqua vs.
A. striata and
A. obliqua vs.
A. serpentina, with higher Jaccard indices (0.6064 and 0.6316, respectively). In the El Neutro episode, the comparisons with the best environmental similarity were
A. serpentina vs.
A. striata and
A. obliqua vs.
A. striata, which presented higher Jaccard indices (0.4616 and 0.6411, respectively). In the La Niña episode, the comparisons that presented the best environmental similarity were
A. obliqua vs.
A. serpentina and
A. obliqua vs.
A. striata, with higher Jaccard indices (0.5982 and 0.6228, respectively). Likewise, our results present the risk maps for the establishment of these species throughout the Neotropics, allowing us to predict the level of risk in order to develop integrated pest management plans.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT