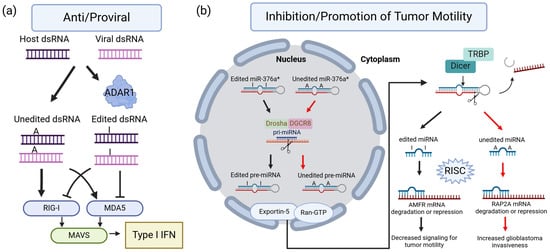
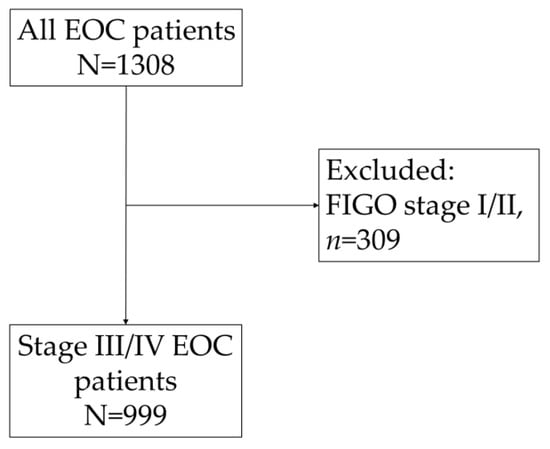
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) can originate from acinar-to-ductal metaplasia (ADM). Pancreatic acini harboring oncogenic
Kras mutations are transdifferentiated to a duct-like phenotype that further progresses to become pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) lesions, giving rise to PDAC. Although ADM formation is frequently observed in
[...] Read more.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) can originate from acinar-to-ductal metaplasia (ADM). Pancreatic acini harboring oncogenic
Kras mutations are transdifferentiated to a duct-like phenotype that further progresses to become pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) lesions, giving rise to PDAC. Although ADM formation is frequently observed in Kras
G12D transgenic mouse models of PDAC, the exact mechanisms of how oncogenic Kras
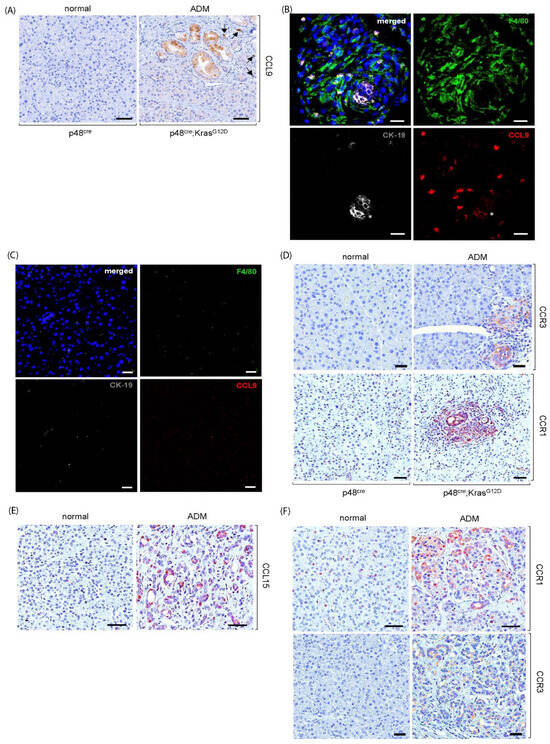
G12D regulates this process remain an enigma. Herein, we revealed a new downstream target of oncogenic Kras, cytokine CCL9, during ADM formation. Higher levels of CCL9 and its receptors, CCR1 and CCR3, were detected in ADM regions of the pancreas in p48
cre:Kras
G12D mice and human PDAC patients. Knockdown of CCL9 in Kras
G12D-expressed pancreatic acini reduced Kras
G12D-induced ADM in a 3D organoid culture system. Moreover, exogenously added recombinant CCL9 and overexpression of CCL9 in primary pancreatic acini induced pancreatic ADM. We also showed that, functioning as a downstream target of Kras
G12D, CCL9 promoted pancreatic ADM through upregulation of the intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and metalloproteinases (MMPs), including MMP14, MMP3 and MMP2. Blockade of MMPs via its generic inhibitor GM6001 or knockdown of specific MMP such as MMP14 and MMP3 decreased CCL9-induced pancreatic ADM. In p48
cre:Kras
G12D transgenic mice, blockade of CCL9 through its specific neutralizing antibody attenuated pancreatic ADM structures and PanIN lesion formation. Furthermore, it also diminished infiltrating macrophages and expression of MMP14, MMP3 and MMP2 in the ADM areas. Altogether, our results provide novel mechanistic insight into how oncogenic Kras enhances pancreatic ADM through its new downstream target molecule, CCL9, to initiate PDAC.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT