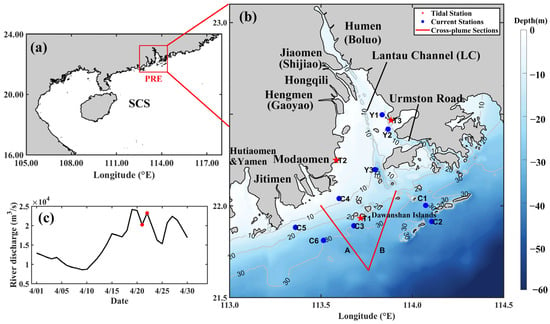
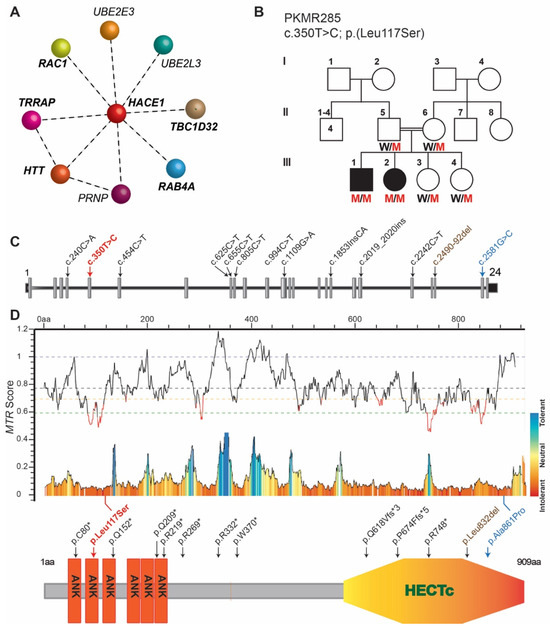
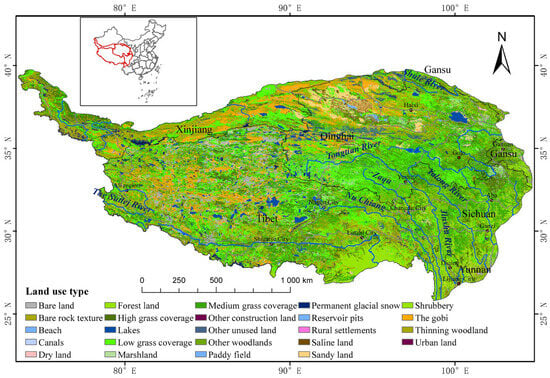
Interactions between carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P), the vital indicators of ecological restoration, play an important role in signaling the health of ecosystems. Rapidly and accurately mapping foliar C, N, and P is essential for interpreting community structure, nutrient limitation, and
[...] Read more.
Interactions between carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P), the vital indicators of ecological restoration, play an important role in signaling the health of ecosystems. Rapidly and accurately mapping foliar C, N, and P is essential for interpreting community structure, nutrient limitation, and primary production during ecosystem recovery. However, research on how to rapidly map C, N, and P in restored areas with mixed plant communities is limited. This study employed laser imaging, detection, and ranging (LiDAR) and hyperspectral data to extract spectral, textural, and height features of vegetation as well as vegetation indices and structural parameters. Causal band, multiple linear regression, and random forest models were developed and tested in a restored area in northern China. Important parameters were identified including (1), for C, red-edge bands, canopy height, and vegetation structure; for N, textural features, height percentile of 40–95%, and vegetation structure; for P, spectral features, height percentile of 80%, and 1 m foliage height diversity. (2) R
2 was used to compare the accuracy of the three models as follows: R
2 values for C were 0.07, 0.42, and 0.56, for N they were 0.20, 0.48, and 0.53, and for P they were 0.32, 0.39, and 0.44; the random forest model demonstrated the highest accuracy. (3) The accuracy of the concentration estimates could be ranked as C > N > P. (4) The inclusion of LiDAR features significantly improved the accuracy of the C concentration estimation, with increases of 22.20% and 47.30% in the multiple linear regression and random forest models, respectively, although the inclusion of LiDAR features did not notably enhance the accuracy of the N and P concentration estimates. Therefore, LiDAR and hyperspectral data can be used to effectively map C, N, and P concentrations in a mixed plant community in a restored area, revealing their heterogeneity in terms of species and spatial distribution. Future efforts should involve the use of hyperspectral data with additional bands and a more detailed classification of plant communities. The application of this information will be useful for analyzing C, N, and P limitations, and for planning for the maintenance of restored plant communities.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT