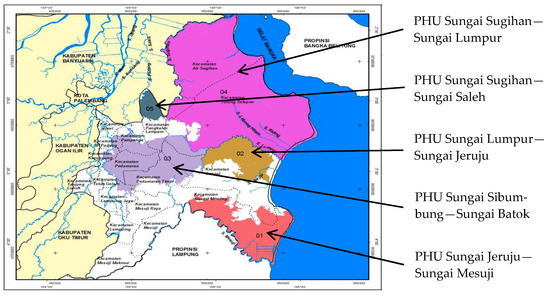
Background and Objectives: mortality and morbidity due to cardiovascular causes are frequently experienced in amputees. Research on the effects of chronic exercise on biomarkers and cardiac damage indicators in these individuals is limited. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of a core training program on brain natriuretic-related peptide, as well as hematological and biochemical parameters in amputee soccer players.
Materials and Methods: The participants were randomly allocated to the following two groups: a core exercise group (CEG) and a control group (CG). While the CG continued routine soccer training, the CEG group was included in a core exercise program different from this group. During the study, routine hemogram parameters of the participants, various biochemical markers, and the concentration of brain natriuretic-related peptide (NT-pro-BNP) were analyzed.
Results: after the training period, notable improvements in various hematological parameters were observed in both groups. In the CEG, there were significant enhancements in red blood cell count (RBC), hematocrit (HCT), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) values. Similarly, the CG also showed substantial improvements in RBC, HCT, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), MCHC, MCH, red cell distribution width-standard deviation (RDW-SD), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLCR), mean platelet volume (MPV), and platelet distribution width (PDW). Moreover, in the CEG, serum triglycerides (TG) and maximal oxygen uptake (MaxVO
2) exhibited significant increases. Conversely, TG levels decreased in the CG, while high-density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and MaxVO
2 levels demonstrated substantial elevations. Notably, the N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels did not undergo significant changes in either the CEG or the CG following the core exercise program (
p > 0.05). However, in the CEG, a meaningful positive correlation was observed between NT-pro-BNP and creatine kinase (CK) levels before and after the core exercise program.
Conclusions: the findings emphasized the potential benefits of core training in enhancing specific physiological aspects, such as erythrocyte-related parameters and lipid metabolism, as well as aerobic capacity. Furthermore, the observed correlation between NT-pro-BNP and CK levels in the CEG provides intriguing insights into the unique physiological adaptations of amputee athletes.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT