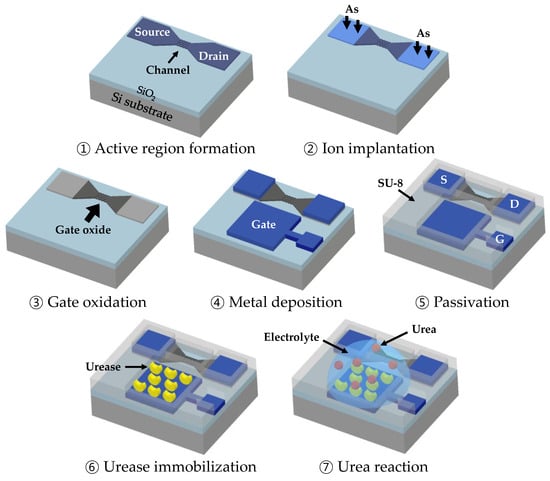
Widespread adoption of mpMRI has led to a decrease in the number of patients requiring prostate biopsies.
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT has demonstrated added benefits in identifying csPCa. Integrating the use of these imaging techniques may hold promise for predicting the presence of csPCa without invasive biopsy. A retrospective analysis of 42 consecutive patients who underwent mpMRI,
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT, prostatic biopsy, and radical prostatectomy (RP) was carried out. A lesion-based model (
n = 122) using prostatectomy histopathology as reference standard was used to analyze the accuracy of
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT, mpMRI alone, and both in combination to identify ISUP-grade group ≥ 2 lesions.
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT demonstrated greater specificity and positive predictive value (PPV), with values of 73.3% (vs. 40.0%) and 90.1% (vs. 82.2%), while the mpMRI Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) 4–5 had better sensitivity and negative predictive value (NPV): 90.2% (vs. 78.5%) and 57.1% (vs. 52.4%), respectively. When used in combination, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV were 74.2%, 83.3%, 93.2%, and 51.0%, respectively. Subgroup analysis of PI-RADS 3, 4, and 5 lesions was carried out. For PI-RADS 3 lesions,
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT demonstrated a NPV of 77.8%. For PI-RADS 4–5 lesions,
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT achieved PPV values of 82.1% and 100%, respectively, with an NPV of 100% in PI-RADS 5 lesions. A combination of
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT and mpMRI improved the radiological diagnosis of csPCa. This suggests that avoidance of prostate biopsy prior to RP may represent a valid option in a selected subgroup of high-risk patients with a high suspicion of csPCa on mpMRI and
68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT