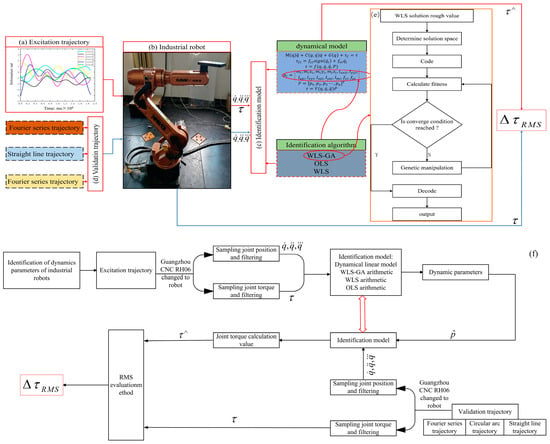
Forty-eight Pelibuey × Katahdin male intact lambs (25.12 ± 3.79 kg LW) were used in a 70-d growing-finishing trial. Dietary treatments consisted of total mixed corn-based diet supplemented with: (1) no feed additives (Control); (2) 150 mg of essential oils blend plus 0.10 mg of 25-hydroxy-Vit-D3/kg diet offered throughout the 70-d experimental period (EOD3); (3) Control diet fed during the first 35 days and zilpaterol hydrochloride (ZH) supplementation at 6 mg/kg diet offered during the final 35 days of the experiment (32 days with ZH with a withdrawal 3-d before harvest), and (4) basal diet supplemented with EOD3 during first 35 days finishing, and EOD3 in combination with ZH (EOD3 + ZH) during the subsequent 32-days with ZH withdrawal 3 days before harvest. The temperature–humidity index during the experiment averaged 80.4 ± 3.2. There were no treatment interactions (
p > 0.20) on growth performance and carcass measures. Supplemental EOD3 did not affect (
p = 0.43) dry matter intake (DMI), but increased (
p < 0.01) carcass adjusted average daily gain (ADG, 9.2%), gain efficiency (GF, 6.7%), and observed vs. expected dietary net energy for maintenance (NE
m, 4.8%) and for gain (NE
g, 6.4%). Supplemental ZH did not affect dry matter intake (DMI,
p = 0.50) but increased (
p < 0.01) carcass adjusted ADG (14.5%), GF (13%) and observed vs. expected dietary NE
m (9%) and NE
g (11.7%). Compared to control lambs, the combination of both additives increased ADG (24.9%), GF (21.2%), and observed vs. expected dietary NE
m and NE
g (14.2% and 18.9%, respectively). There were no treatment interactions on carcass characteristics, visceral organ mass, or on gene expression of IGF1, IGF2 and mTOR in longissimus muscle (LM). Supplemental EOD3 increased hot carcass weight (HCW; 4.0%,
p < 0.01) but did not affect other carcass measures. Supplemental EOD3 decreased (3%,
p = 0.03) intestine mass weight (g intestine/kg empty body weight). Supplemental ZH increased HCW (6%,
p < 0.01), dressing percentage (1.7%,
p = 0.04), and LM area (9.7%,
p < 0.01), and decreased kidney-pelvic-fat percentage (16.2%,
p < 0.01), fat thickness (14.7%,
p = 0.03), and visceral fat. Compared to controls, the combination of EOD3 with ZH increased HCW (10.2%). It is concluded that growth performance responses to supplemental EOD3 and ZH are additive. Both supplements can be fed in combination without detrimental effects on expected benefits when fed separately. In addition, ZH supplementation improves carcass traits.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT