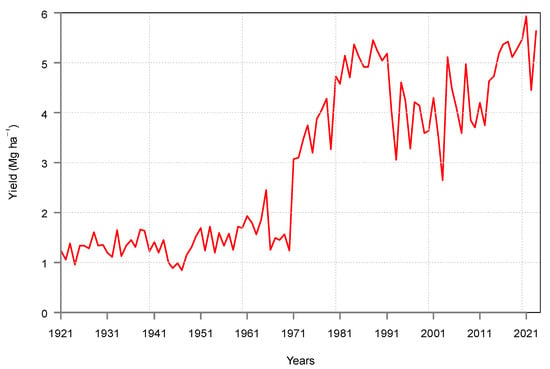
Objective: To assess the association between pretreatment thrombocytosis, anemia, and leukocytosis and overall survival (OS) of advanced-stage EOC. Furthermore, to develop nomograms using established prognostic factors and pretreatment hematologic parameters to predict the OS of advanced EOC patients.
Methods: Advanced-stage EOC patients
[...] Read more.
Objective: To assess the association between pretreatment thrombocytosis, anemia, and leukocytosis and overall survival (OS) of advanced-stage EOC. Furthermore, to develop nomograms using established prognostic factors and pretreatment hematologic parameters to predict the OS of advanced EOC patients.
Methods: Advanced-stage EOC patients treated between January 1996 and January 2010 in eastern Netherlands were included. Survival outcomes were compared between patients with and without pretreatment thrombocytosis (≥450,000 platelets/µL), anemia (hemoglobin level of <7.5 mmol/L), or leukocytosis (≥11.0 × 10
9 leukocytes/L). Three nomograms (for ≤3-, ≥5-, and ≥10-year OS) were developed. Candidate predictors were fitted into multivariable logistic regression models. Multiple imputation was conducted. Model performance was assessed on calibration, discrimination, and Brier scores. Bootstrap validation was used to correct for model optimism.
Results: A total of 773 advanced-stage (i.e., FIGO stages IIB–IV) EOC patients were included. The median [interquartile range, IQR] OS was 2.3 [1.3–4.2] and 3.0 [1.4–7.0] years for patients with and without pretreatment thrombocytosis (
p < 0.01). The median OS was not notably different for patients with and without pretreatment leukocytosis (
p = 0.58) or patients with and without pretreatment anemia (
p = 0.07). The final nomograms comprised established predictors with either pretreatment leukocyte or platelet count. The ≥5- and ≥10-year OS models demonstrated good calibration and adequate discrimination with optimism-corrected
c-indices [95%-CI] of 0.76 [0.72–0.80] and 0.78 [0.73–0.83], respectively. The ≤3-year OS model demonstrated suboptimal performance with an optimism-corrected c-index of 0.71 [0.66–0.75].
Conclusions: Pretreatment thrombocytosis is associated with poorer EOC survival. Two well-performing models predictive of ≥5-year and ≥10-year OS in advanced-stage EOC were developed and internally validated.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT