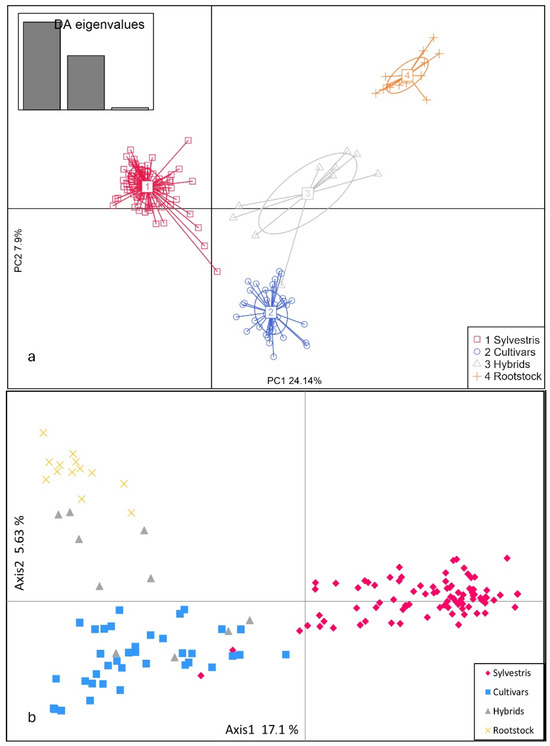
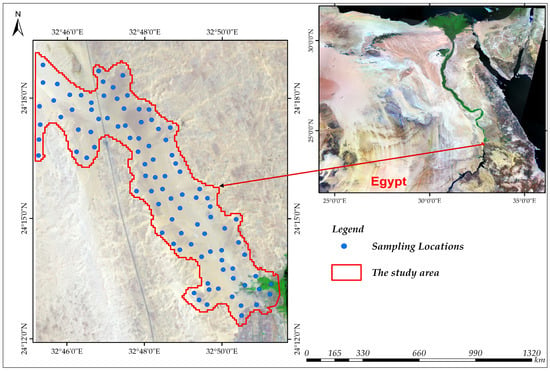
Estimating soil erodible fraction based on basic soil properties in arid lands is a valuable research topic in the field of soil science and land management. The Proximal Sensing (PS) technique offers a non-destructive and efficient method to assess wind erosion potential in arid regions. By using Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) models and combining soil texture and chemical properties, determined through Visible-Near Infrared (vis-NIR) spectroscopy in 96 soil samples, this study aims to predict soil erodibility, soil organic matter (SOM), and calcium carbonate equivalent (CaCO
3) in arid lands located in Elkobaneyya Valley, Aswan Governorate, Egypt. Results showed that the soil erodibility fraction (EF-Factor) had the highest values and possessed a strong relationship between slope and SOM of 0.01% in determining soil erodibility. The PLSR model performed better than SVM for estimating SOM, CaCO
3, and EF-Factor. Furthermore, the results showed that the spectral responses of CaCO
3 were observed in separate places in the wavelengths of 570, 649, 802, 1161, 1421, 1854, and 2362 nm, and the wavelengths with SOM parameter were 496, 658, 779, 1089, 1417, 1871, and 2423 nm. The EF-factor shows the highest significant correlation with spectral reflectance values at 526, 688, 744, 1418, 1442, 2292, and 2374 nm. The accuracy and performance of the PLSR model in estimating the EF-Factor using spectral reflectance data and the distribution of data points for both the calibration and validation data-sets indicate a good accuracy of the PLSR model, with RMSE values of 0.0921 and 0.0836 Mg h MJ
−1 mm
−1, coefficient of determination (R
2) values of 0.931 and 0.76, and RPD values of 2.168 and 2.147, respectively.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT