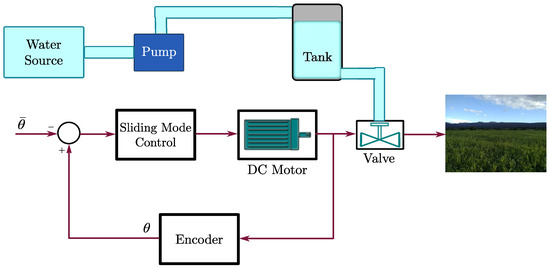
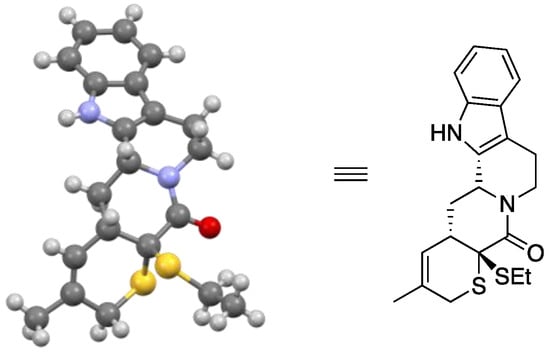
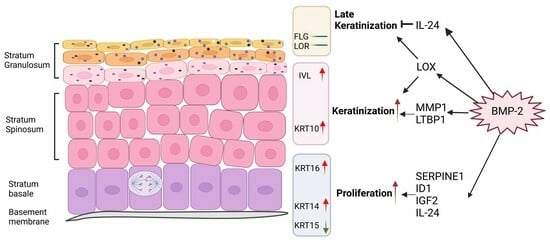
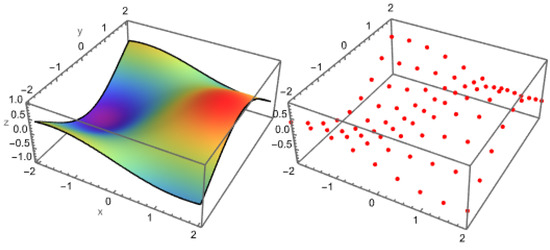
Background: Burns represent a serious health problem, associated with multiple-organ failure, prolonged hospitalization, septic complications, and increased rate of mortality. The main aim of our study was to evaluate the levels of various circulating molecules in children with severe burns (more than
[...] Read more.
Background: Burns represent a serious health problem, associated with multiple-organ failure, prolonged hospitalization, septic complications, and increased rate of mortality. The main aim of our study was to evaluate the levels of various circulating molecules in children with severe burns (more than 25% TBSA), in three different moments: 48 h, day 10, and day 21 post-burn.
Materials and Methods: This study included 32 children with burns produced by flame, hot liquid, and electric arc and 21 controls. Serum plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), α 1-acid glycoprotein (AGP), C-reactive protein (CRP), and platelet factor 4 (PF4) were detected using the Multiplex technique. Several parameters, such as fibrinogen, leucocyte count, thrombocyte count, triiodothyronine, thyroxine, and thyroid-stimulating hormone were also determined for each patient during hospitalization.
Results: Significant statistical differences were obtained for CRP, AGP, and PF4 compared to the control group, in different moments of measurements. Negative correlations between CRP, AGP, and PF4 serum levels and burned body surface, and also the hospitalization period, were observed.
Discussions: CRP levels increased in the first 10 days after burn trauma and then decreased after day 21. Serum PAI-1 levels were higher immediately after the burn and started decreasing only after day 10 post-burn. AGP had elevated levels 48 h after the burn, then decreased at 7–10 days afterwards, and once again increased levels after 21 days. PF4 serum levels increased after day 10 since the burning event.
Conclusions: Serum CRP, AGP, PAI-1, and PF4 seem to be promising molecules in monitoring patients with a burn within the first 21 days.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT