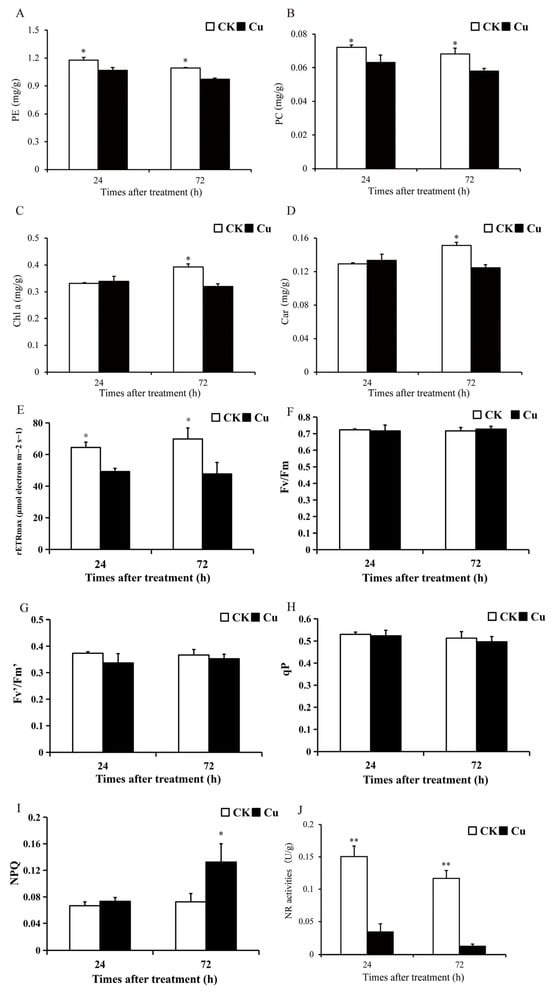
Drug candidates must undergo thermal evaluation as early as possible in the preclinical phase of drug development because undesirable changes in their structure and physicochemical properties may result in decreased pharmacological activity or enhanced toxicity. Hence, the detailed evaluation of nitrogen-rich heterocyclic esters as potential drug candidates, i.e., imidazolidinoannelated triazinylformic acid ethyl esters
1–
3 (where R
1 = 4–CH
3 or 4–OCH
3 or 4–Cl, and R
2 = –COOC
2H
5) and imidazolidinoannelated triazinylacetic acid methyl esters
4–
6 (where R
1 = 4–CH
3 or 4–OCH
3 or 4–Cl, and R
2 = –CH
2COOCH
3)—in terms of their melting points, melting enthalpy values, thermal stabilities, pyrolysis, and oxidative decomposition course—has been carried out, using the simultaneous thermal analysis methods (TG/DTG/DSC) coupled with spectroscopic techniques (FTIR and QMS). It was found that the melting process (documented as one sharp peak related to the solid–liquid phase transition) of the investigated esters proceeded without their thermal decomposition. It was confirmed that the melting points of the tested compounds increased in relation to R
1 and R
2 as follows:
2 (R
1 = 4–OCH
3; R
2 = –COOC
2H
5) <
6 (R
1 = 4–Cl; R
2 = –CH
2COOCH
3) <
5 (R
1 = 4–OCH
3; R
2 = –CH
2COOCH
3) <
3 (R
1 = 4–Cl; R
2 = –COOC
2H
5) <
1 (R
1 = 4–CH
3; R
2 = –COOC
2H
5) <
4 (R
1 = 4–CH
3; R
2 = –CH
2COOCH
3). All polynitrogenated heterocyclic esters proved to be thermally stable up to 250 °C in inert and oxidising conditions, although
1–
3 were characterised by higher thermal stability compared to
4–
6. The results confirmed that both the pyrolysis and the oxidative decomposition of heterocyclic ethyl formates/methyl acetates with
para-substitutions at the phenyl moiety proceed according to the radical mechanism. In inert conditions, the pyrolysis process of the studied molecules occurred with the homolytic breaking of the C–C, C–N, and C–O bonds. This led to the emission of alcohol (ethanol in the case of
1–
3 or methanol in the case of
4–
6), NH
3, HCN, HNCO, aldehydes, CO
2, CH
4, HCl, aromatics, and H
2O. In turn, in the presence of air, cleavage of the C–C, C–N, and C–O bonds connected with some oxidation and combustion processes took place. This led to the emission of the corresponding alcohol depending on the analysed class of heterocyclic esters, NH
3, HCN, HNCO, aldehydes, N
2, NO/NO
2, CO, CO
2, HCl, aromatics, and H
2O. Additionally, after some biological tests, it was proven that all nitrogen-rich heterocyclic esters—as potential drug candidates—are safe for erythrocytes, and some of them are able to protect red blood cells from oxidative stress-induced damage.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT