Objective: The vast majority of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are driven by activating mutations in
KIT,
PDGFRA, or components of the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) complex (
SDHA,
SDHB,
SDHC, and
SDHD genes). A small fraction of GISTs lack
[...] Read more.
Objective: The vast majority of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are driven by activating mutations in
KIT,
PDGFRA, or components of the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) complex (
SDHA,
SDHB,
SDHC, and
SDHD genes). A small fraction of GISTs lack alterations in
KIT,
PDGFRA, and
SDH. We aimed to further characterize the clinical and genomic characteristics of these so-called “triple-negative” GISTs.
Methods: We extracted clinical and genomic data from patients seen at MD Anderson Cancer Center with a diagnosis of GIST and available clinical next generation sequencing data to identify “triple-negative” patients.
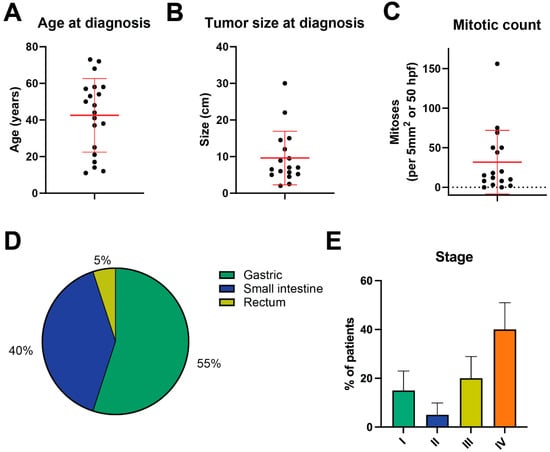
Results: Of the 20 patients identified, 11 (55.0%) had gastric, 8 (40.0%) had small intestinal, and 1 (5.0%) had rectal primary sites. In total, 18 patients (90.0%) eventually developed recurrent or metastatic disease, and 8 of these presented with de novo metastatic disease. For the 13 patients with evaluable response to imatinib (e.g., neoadjuvant treatment or for recurrent/metastatic disease), the median PFS with imatinib was 4.4 months (range 0.5–191.8 months). Outcomes varied widely, as some patients rapidly developed progressive disease while others had more indolent disease. Regarding potential genomic drivers, four patients were found to have alterations in the RAS/RAF/MAPK pathway: two with a
BRAF V600E mutation and two with
NF1 loss-of-function (LOF) mutations (one deletion and one splice site mutation). In addition, we identified two with
TP53 LOF mutations, one with
NTRK3 fusion (
ETV6-NTRK3), one with
PTEN deletion, one with
FGFR1 gain-of-function (GOF) mutation (K654E), one with
CHEK2 LOF mutation (T367fs*), one with Aurora kinase A fusion (
AURKA-CSTF1), and one with
FANCA deletion. Patients had better responses with molecularly targeted therapies than with imatinib.
Conclusions: Triple-negative GISTs comprise a diverse cohort with different driver mutations. Compared to
KIT/
PDGFRA-mutant GIST, limited benefit was observed with imatinib in triple-negative GIST. In depth molecular profiling can be helpful in identifying driver mutations and guiding therapy.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT