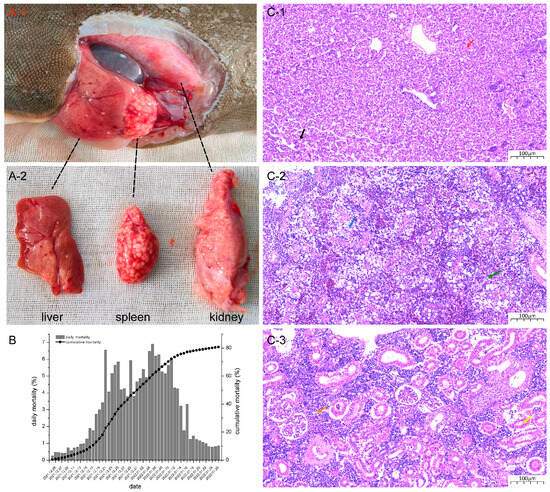
Berberine, a natural alkaloid found abundantly in various medicinal plants, exhibits antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and lipid metabolism-regulatory properties. Nonetheless, its protective effects and the molecular mechanisms underlying liver injury in fish have not been fully elucidated. The aims of this study were to investigate
[...] Read more.
Berberine, a natural alkaloid found abundantly in various medicinal plants, exhibits antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and lipid metabolism-regulatory properties. Nonetheless, its protective effects and the molecular mechanisms underlying liver injury in fish have not been fully elucidated. The aims of this study were to investigate the antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and lipid metabolism-regulating effects of berberine against high-fat diet (HFD)-induced liver damage and to clarify the underlying molecular mechanisms. Tilapia were fed diets containing two doses of berberine (50 and 100 mg/kg diet) alongside high fat for 60 days. The results showed that berberine treatments (50 and/or 100 mg/kg) significantly reduced elevated aminotransferases, triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) in the plasma. In the liver, berberine treatments significantly increased the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (
pparα) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (
cpt-1) genes, leading to a reduction in lipid accumulation. Meanwhile, berberine treatment suppressed lipid peroxidation formation and enhanced antioxidant capacity. Berberine upregulated the mRNA levels of erythroid 2-related factor 2 (
nrf2) and its downstream genes including heme oxygenase 1 (
ho-1) and glutathione-S-transferase (
gstα). Additionally, berberine attenuated the inflammation by inhibiting the expression of toll-like receptor 2 (
tlr2), myeloid differential protein-88 (
myd88),
relb, and inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (
il-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α (
tnf-α), and
il-8. In summary, this study suggested that berberine offers protection against HFD-induced liver damage in tilapia via regulating lipid metabolism, antioxidant status, and immune response. This protective effect may be attributed to the modulation of the Nrf2, TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB, and PPARα signaling pathways.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT