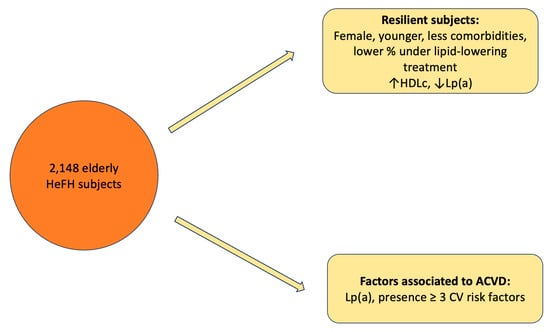
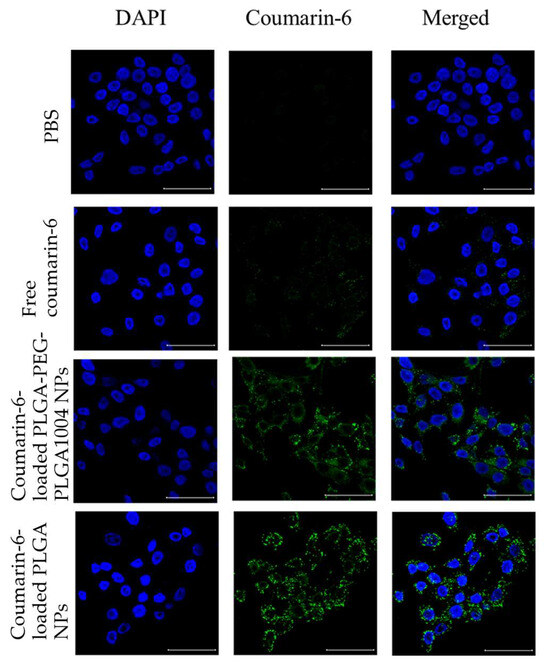
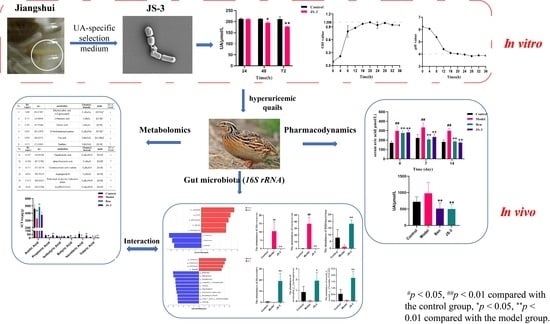
Background: A diet high in purines can impair the function of the gut microbiota and disrupt purine metabolism, which is closely associated with the onset of hyperuricemia. Dietary regulation and intestinal health maintenance are key approaches for controlling uric acid (UA) levels. Investigating the impacts of fermented foods offers potential dietary interventions for managing hyperuricemia.
Methods: In this study, we isolated a strain with potent UA-degrading capabilities from “Jiangshui”, a fermented food product from Gansu, China. We performed strain identification and assessed its probiotic potential. Hyperuricemic quails, induced by a high-purine diet, were used to assess the UA degradation capability of strain JS-3 by measuring UA levels in serum and feces. Additionally, the UA degradation pathways were elucidated through analyses of the gut microbiome and fecal metabolomics.
Results: JS-3, identified as
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, was capable of eliminating 16.11% of uric acid (UA) within 72 h, rapidly proliferating and producing acid within 12 h, and surviving in the gastrointestinal tract. Using hyperuricemic quail models, we assessed JS-3’s UA degradation capacity. Two weeks after the administration of JS-3 (2 × 10
8 cfu/d per quail), serum uric acid (SUA) levels significantly decreased to normal levels, and renal damage in quails was markedly improved. Concurrently, feces from the JS-3 group demonstrated a significant degradation of UA, achieving up to 49% within 24 h.
16S rRNA sequencing revealed JS-3’s role in gut microbiota restoration by augmenting the probiotic community (
Bifidobacterium,
Bacteroides unclassified_f-Lachnospiraceae, and
norank_fynorank_o-Clostridia_UCG-014) and diminishing the pathogenic bacteria (
Macrococus and
Lactococcus). Corresponding with the rise in short-chain fatty acid (SCFA)-producing bacteria, JS-3 significantly increased SCFA levels (
p < 0.05, 0.01). Additionally, JS-3 ameliorated metabolic disturbances in hyperuricemic quails, influencing 26 abnormal metabolites predominantly linked to purine, tryptophan, and bile acid metabolism, thereby enhancing UA degradation and renal protection.
Conclusions: For the first time, we isolated and identified an active probiotic strain, JS-3, from the “Jiangshui” in Gansu, used for the treatment of hyperuricemia. It modulates host–microbiome interactions, impacts the metabolome, enhances intestinal UA degradation, reduces levels of SUA and fecal UA, alleviates renal damage, and effectively treats hyperuricemia without causing gastrointestinal damage. In summary, JS-3 can serve as a probiotic with potential therapeutic value for the treatment of hyperuricemia.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT