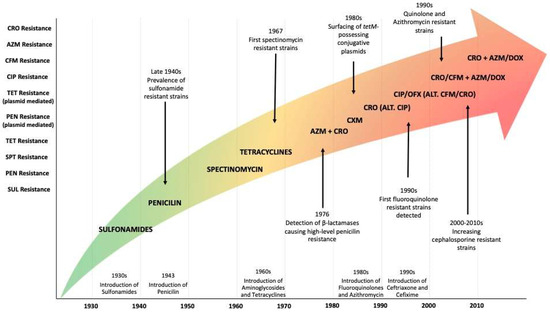
Background and Objectives: Leukemia, characterized by abnormal leukocyte production, exhibits clonal origin from somatic mutations. Globally, it ranked 15th in cancer incidence in 2020, with higher prevalence in developing countries. In Mexico, it was the ninth most frequent cancer. Regional registries are
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Leukemia, characterized by abnormal leukocyte production, exhibits clonal origin from somatic mutations. Globally, it ranked 15th in cancer incidence in 2020, with higher prevalence in developing countries. In Mexico, it was the ninth most frequent cancer. Regional registries are vital for understanding its epidemiology. This study aims to analyze the prevalence and age-standardized incidence rates of leukemias in a tertiary care hospital in the Mexican Bajio region.
Materials and Methods: Leukemia cases from 2008–2018 were analyzed, and 535 medical records were included in this study. The prevalence, distribution, and age-specific incidence rate of different types and subtypes of leukemia were determined according to sex and age groups.
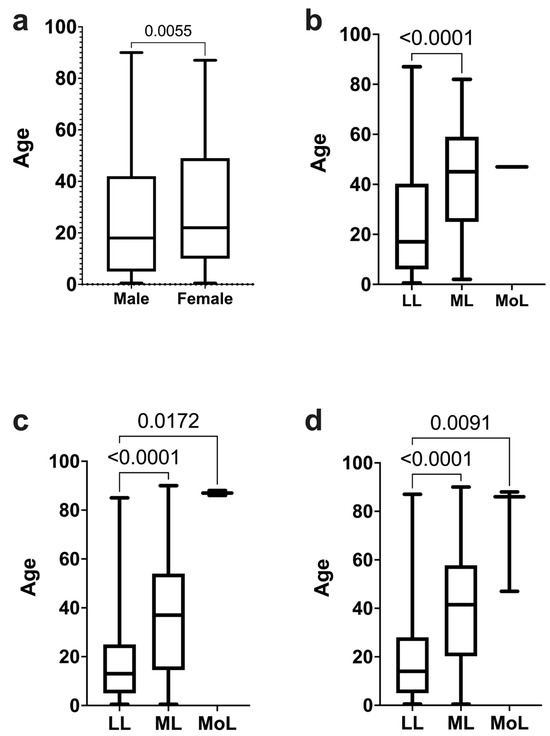
Results: Overall, 65.79% consisted of lymphocytic leukemia, 33.64% of myeloid leukemia, and 0.56% of monocytic leukemia. No significant sex-based differences were found, but age-specific patterns were observed. Leukemia distribution by age revealed significant associations. Lymphocytic leukemia dominated in the pediatric population, particularly acute lymphocytic leukemia, while myeloid leukemia shifted towards adulthood. Age-specific incidence patterns showed, first, that lymphocytic leukemia is the most common leukemia in pediatric ages, and second, there is a shift from acute lymphocytic leukemia dominance in pediatric ages to myeloid leukemia incidence in late adulthood, emphasizing nuanced epidemiological dynamics.
Conclusions: Acute leukemia cases occurred with high prevalence in our study population, with a high incidence in pediatric and adulthood populations, especially for acute lymphocytic leukemia, showing a (<18 years) 153.8 age-standardized incidence rate in the pediatric group, while in the adult population, the age-standardized rate was 59.84. In the age-specific analysis, we found that the childhood group (5–9 years) were the most affected by acute lymphocytic leukemia in the pediatric population, while in the adult population, the early-adulthood group (15–29 years) were the most affected age group. In contrast, chronic myeloid leukemia affected both adults and the pediatric populations, while chronic lymphocytic leukemia and monocytic leukemia were exclusive to adults. The study underscores the need for tailored diagnostic, treatment, and preventive strategies based on age, contributing valuable insights into the leukemia epidemiology of the Bajio region.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT