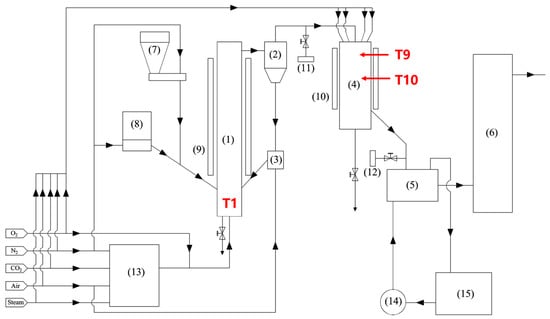
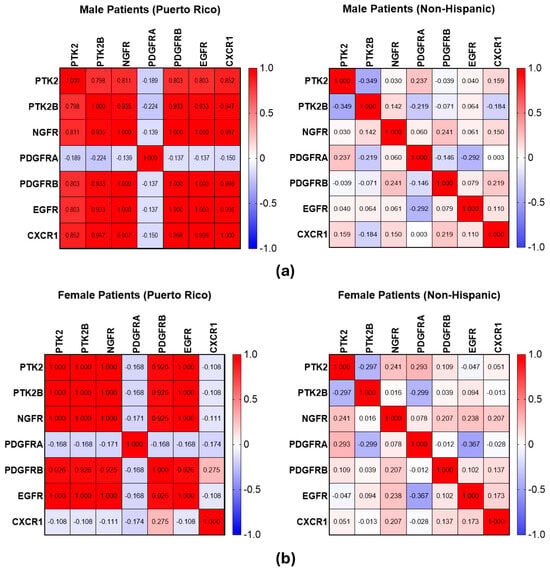
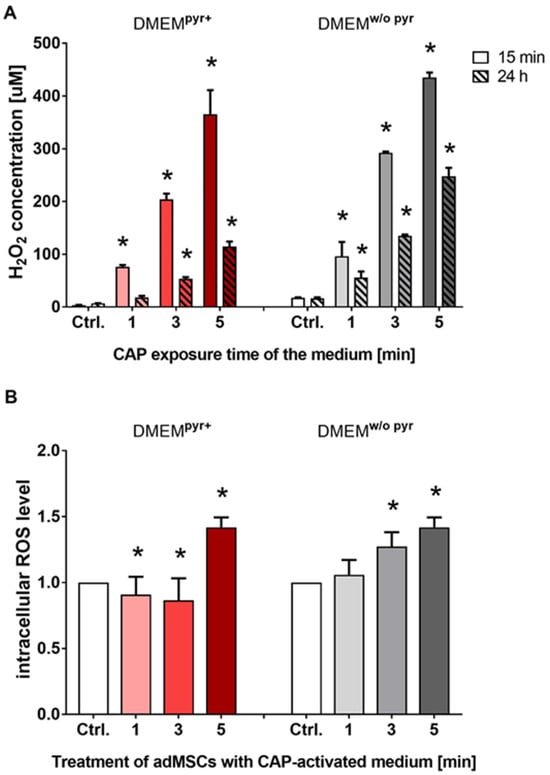
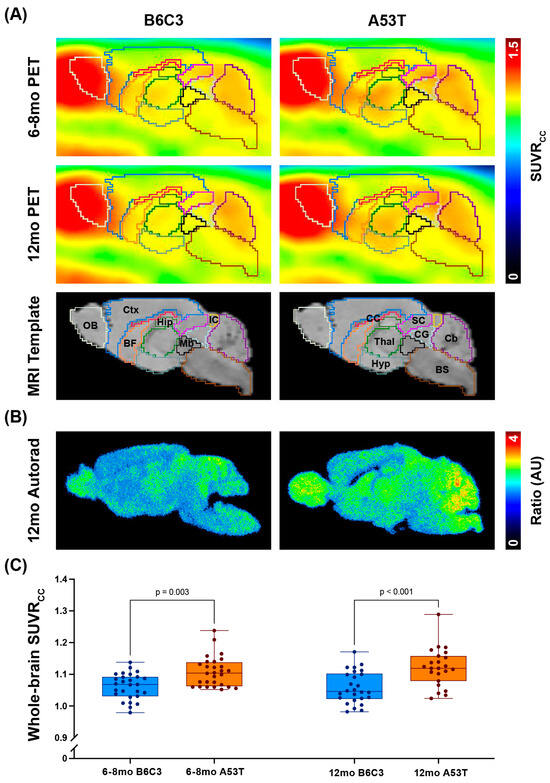
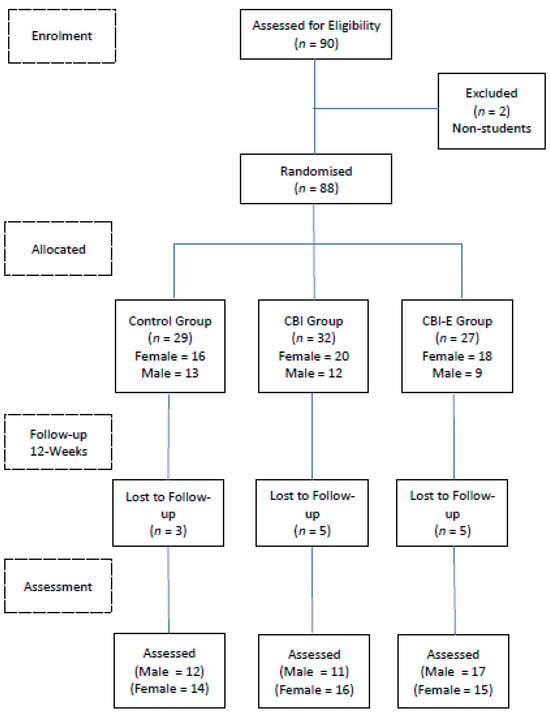
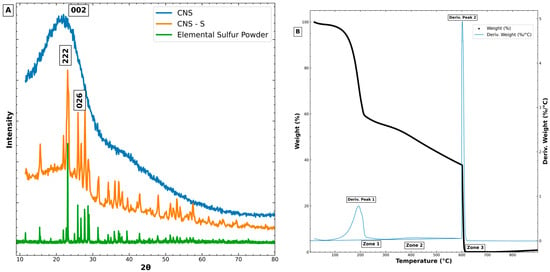
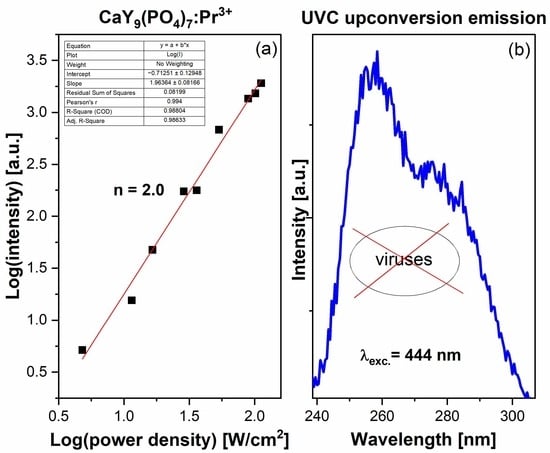
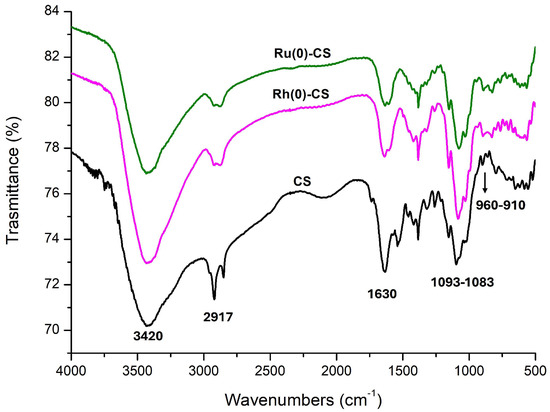
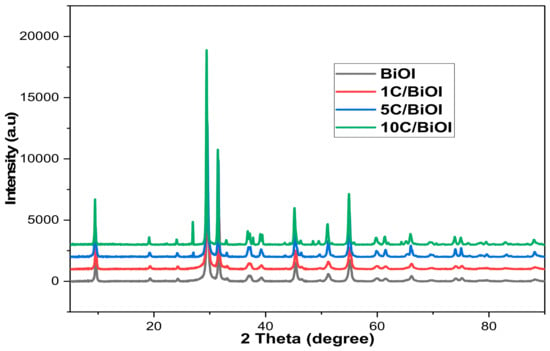
For achieving CO
2 thermal reduction, a technology combining solid carbon activation and high-temperature CO
2 reduction was proposed, named as activated-reduction technology. In this study, this technology is realized by using a circulating fluidized bed and downdraft reactor. Reduced agent parameters (O
[...] Read more.
For achieving CO
2 thermal reduction, a technology combining solid carbon activation and high-temperature CO
2 reduction was proposed, named as activated-reduction technology. In this study, this technology is realized by using a circulating fluidized bed and downdraft reactor. Reduced agent parameters (O
2/C and CO
2 concentration) greatly affect the reduction effect of CO
2. In addition, the effect of the activation process on different carbon-based materials can help to broaden the range of carbon-based materials used for CO
2 reduction, which is also an important issue. The following three points have been studied through experiments: (1) the influence of the characteristics of the reduced agent (CO
2 concentration and O
2/C) on CO
2 reduction; (2) the performance of different chars in CO
2 reduction; and (3) the activation effect of solid carbon. The activation process can develop the pore structure of coal gasification char and transform it into activated char with higher reactivity. The CO concentration in the tail gas is a crucial factor limiting the effectiveness of CO
2 reduction, with an experimentally determined upper limit of around 55% at 1200 °C. If CO concentration is far from the upper limit, temperature becomes the significant influencing factor. When the reduced agent O
2/C is 0.18, the highest net CO
2 reduction of 0.021 Nm
3/kg is achieved at 60% CO
2 concentration. When the reduced agent CO
2 concentration is 50%, the highest net CO
2 reduction of 0.065 Nm
3/kg is achieved at 0.22 O
2/C. Compared with CPGC, YHGC has higher reactivity and is more suitable for CO
2 reduction. The activation process helps to reduce the differences between raw materials.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT