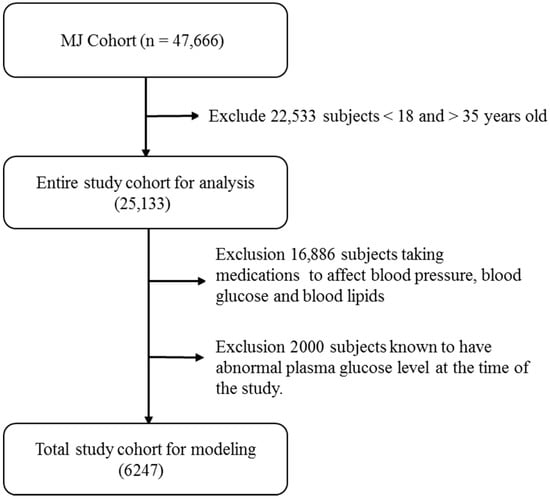
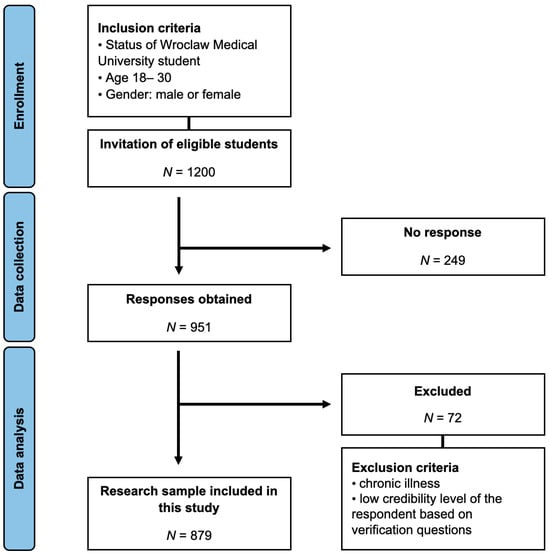
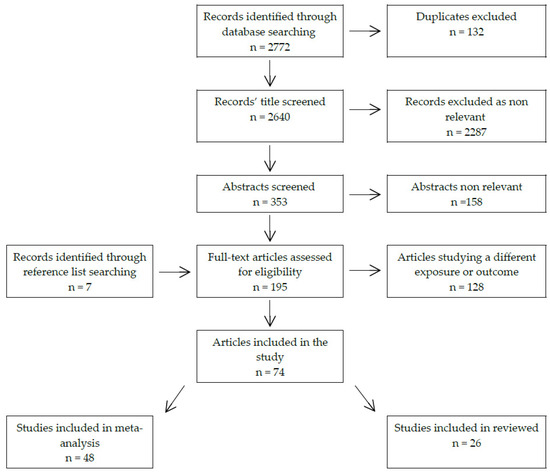
Nickel-element-doped zinc cobaltate/carbon fiber composites (Ni-ZnCo
2O
4/CF) were prepared on carbon cloth (made of a combination of carbon fibers) conductive substrates using a simple ambient stirring method combined with heat treatment. Characterization tests of the materials revealed that the prepared products were porous Ni-ZnCo
2O
4/CF mesh structures. This porous network structure increases the surface area of the material and helps shorten the diffusion path of ions and electrons. The samples were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) methods to investigate the effect of Ni elemental doping on the stability of the materials. The results show that there are no other impurity peaks and no other impurity elements in the Ni-ZnCo
2O
4/CF electrode material, which indicates that the sample purity is high. Meanwhile, the electrochemical properties of Ni-ZnCo
2O
4/CF electrode materials were studied. Under the condition of 15 A·g
−1, the specific capacitance of Ni-ZnCo
2O
4/CF electrode material is 1470 F·g
−1, and after 100 cycles, its specific capacity reaches 1456 F·g
−1, which is 99.0% of the specific capacity of 1470 F·g
−1, indicating that the electrode material has good stability. In addition, we assembled asymmetric supercapacitors (Ni-ZnCo
2O
4/CF//CNTs) with Ni-ZnCo
2O
4/CF as the positive material and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as the negative material. In the cyclic stability experiment of Ni-ZnCo
2O
4/CF/CNTs devices, when the current density was 1 A·g
−1, the specific capacitance was 182 F·g
−1. After 10,000 cyclic charge–discharge tests, the specific capacity became 167 F·g
−1, which was basically unchanged compared with the initial specific capacity, reaching 91.8%. It shows that it has higher charge–discharge performance and higher cycle stability.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT