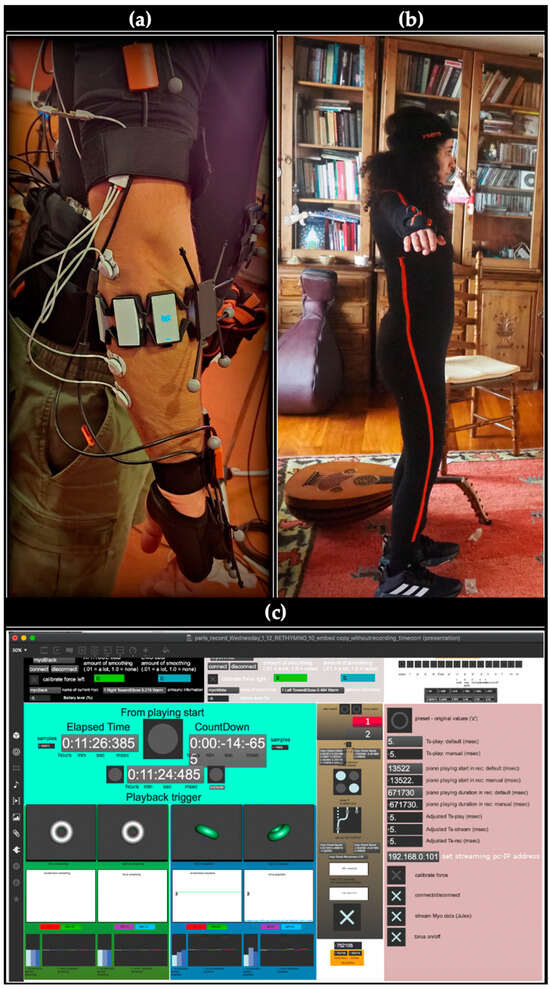
In an attempt to reutilize marble waste, a new approach is presented in the current study to promote its use in the field of shielding against ionizing radiation. In this study, we aimed to develop a novel and sustainable/eco-friendly lead-free radiation shielding material by improving artificial marble (AM) produced from marble waste combined with polyester by reinforcing it with bismuth oxide (Bi
2O
3) nanoparticles. Six samples of AM samples doped with different concentrations (
,
,
,
,
, and
) of Bi
2O
3 nanoparticles were prepared. The linear attenuation coefficient (
) values were measured experimentally through the narrow beam method at different energies
,
,
, and
) for all samples with various concentrations of Bi
2O
3. Radiological shielding parameters such as half value layer (
), tenth-value layer (
), and radiation shielding efficiency (
) were estimated and compared for all the different samples. The results prove that increasing the concentration of Bi
2O
3 leads to the enhancement of the radiation shielding properties of the AM as a shielding material. It was observed that as the energy increases, the efficiency of the samples falls. High energy dependence was found when calculating the
and
values of the samples, which increased with increases in the energy of the incident photons. A comparison between the sample with the most efficient gamma radiation attenuation capability (AM-
), concrete, and lead was conducted, and a discussion regarding their radiation shielding properties is presented herein. The results show that the AM-
sample is superior to the ordinary concrete over all the studied energy ranges, as evidenced by its significantly lower
. On the contrary, lead is superior to the AM-
sample over all the studied energy ranges owing to its unbeatable density as a shielding material. Overall, this new type of artificial marble has the potential to be used as a radiation shielding material at low- to medium-gamma energy regions, specifically in medical imaging and radiation therapy.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT