Background and Objectives: Chronic radiotherapy-induced skin injury (cRISI) is an irreversible and progressive condition that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Despite the limited literature available on the assessment of the epidermal barrier in cRISI, there is a consensus that appropriate skincare, including the use of emollients, is the primary therapeutic approach for this group of patients. The aim of this study was to evaluate the biophysical properties of the skin during the late period (at least 90 days) following radiation therapy (RT) for head and neck cancer.
Materials and Methods: This was a single-center prospective non-randomized study. It involved the analysis of 16 adult patients with head and neck cancer who underwent RT at the Greater Poland Cancer Center, along with 15 healthy volunteers. The study and control groups were matched for gender and age (
p = 0.51). Clinical assessment, based on the LENT-SOMA scale, was conducted for all patients. Evaluation of the skin’s biophysical properties included: an analysis of transepidermal water loss (TEWL), stratum corneum hydration (SCH), and skin visualization using high-frequency ultrasonography (HF-USG).
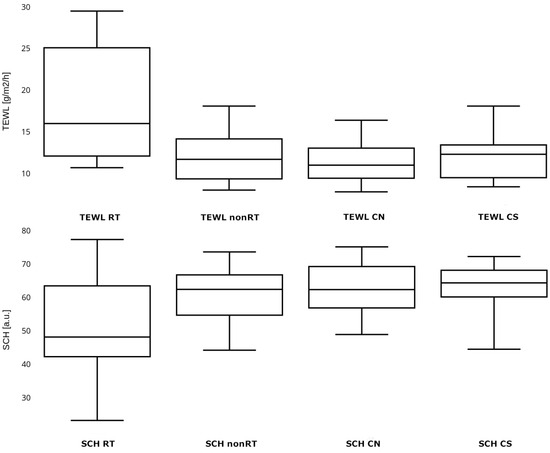
Results: A significantly higher TEWL was observed in the irradiated area compared to the control area in the study group (
p = 0.004). However, there was no statistically significant difference in SCH (
p = 0.073). Additionally, no significant difference was observed in the values of TEWL and SCH in the irradiated area between the group of patients with and without clinically obvious RISI (
p = 0.192 and
p = 0.415, respectively). The skin thickness of the irradiated area, assessed by HF-USG, did not differ significantly from the skin thickness of the control area (
p = 0.638). Furthermore, no difference in skin thickness was observed in patients with clinical features of cRISI in the irradiated and control areas (
p = 0.345). The mean time after RT was 6.1 years.
Conclusions: This study marks the first demonstration of epidermal barrier damage in patients in the long term following RT for head and neck cancer. The impairment of the epidermal barrier was observed independently of evident cRISI features. This observation underscores the necessity to recommend appropriate skin care, including the use of emollients, for all patients following RT. We also suggest that HF-USG examination is generally inconclusive in determining the degree of skin damage in the late period after RT.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT