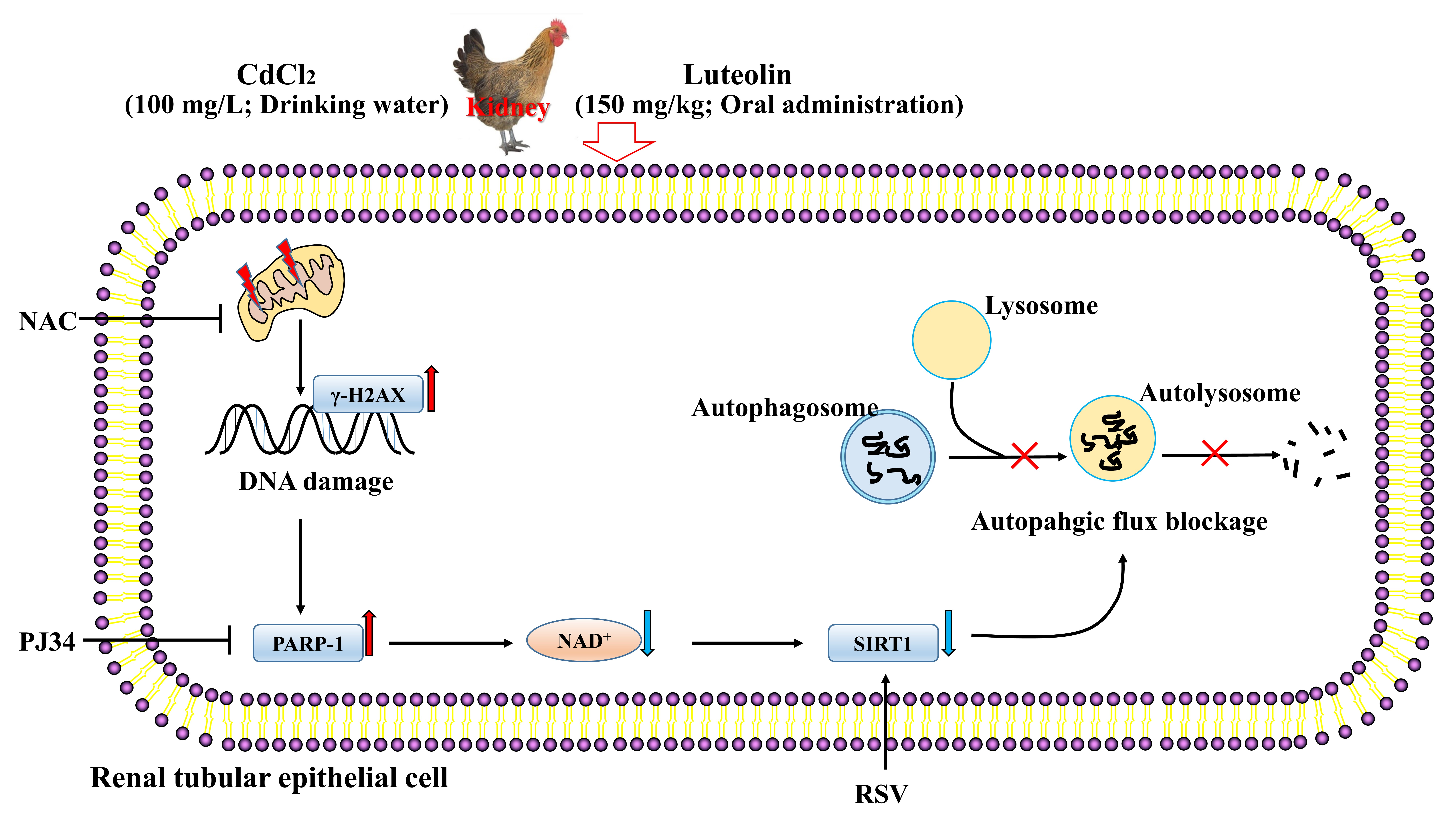
Chickens are a major source of meat and eggs in human food and have significant economic value. Cadmium (Cd) is a common environmental pollutant that can contaminate feed and drinking water, leading to kidney injury in livestock and poultry, primarily by inducing the generation of free radicals. It is necessary to develop potential medicines to prevent and treat Cd-induced nephrotoxicity in poultry. Luteolin (Lut) is a natural flavonoid compound mainly extracted from peanut shells and has a variety of biological functions to defend against oxidative damage. In this study, we aimed to demonstrate whether Lut can alleviate kidney injury under Cd exposure and elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. Renal histopathology and cell morphology were observed. The indicators of renal function, oxidative stress, DNA damage and repair, NAD
+ content, SIRT1 activity, and autophagy were analyzed. In vitro data showed that Cd exposure increased ROS levels and induced oxidative DNA damage and repair, as indicated by increased 8-OHdG content, increased
-H2AX protein expression, and the over-activation of the DNA repair enzyme PARP-1. Cd exposure decreased NAD
+ content and SIRT1 activity and increased LC3 II, ATG5, and particularly p62 protein expression. In addition, Cd-induced oxidative DNA damage resulted in PARP-1 over-activation, reduced SIRT1 activity, and autophagic flux blockade, as evidenced by reactive oxygen species scavenger NAC application. The inhibition of PARP-1 activation with the pharmacological inhibitor PJ34 restored NAD
+ content and SIRT1 activity. The activation of SIRT1 with the pharmacological activator RSV reversed Cd-induced autophagic flux blockade and cell injury. In vivo data demonstrated that Cd treatment caused the microstructural disruption of renal tissues, reduced creatinine, and urea nitrogen clearance, raised MDA content, and decreased the activities or contents of antioxidants (GSH, T-SOD, CAT, and T-AOC). Cd treatment caused oxidative DNA damage and PARP-1 activation, decreased NAD
+ content, decreased SIRT1 activity, and impaired autophagic flux. Notably, the dietary Lut supplement observably alleviated these alterations in chicken kidney tissues induced by Cd. In conclusion, the dietary Lut supplement alleviated Cd-induced chicken kidney injury through its potent antioxidant properties by relieving the oxidative DNA damage-activated PARP-1-mediated reduction in SIRT1 activity and repairing autophagic flux blockade.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT