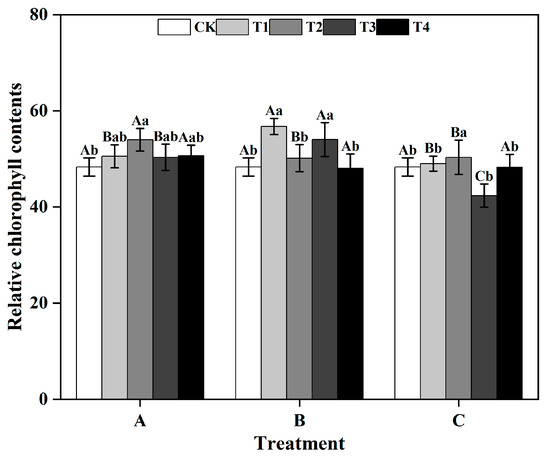
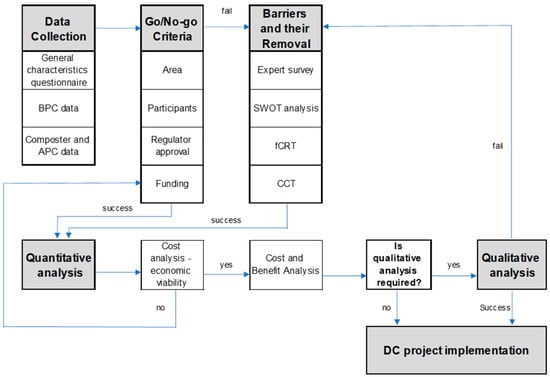
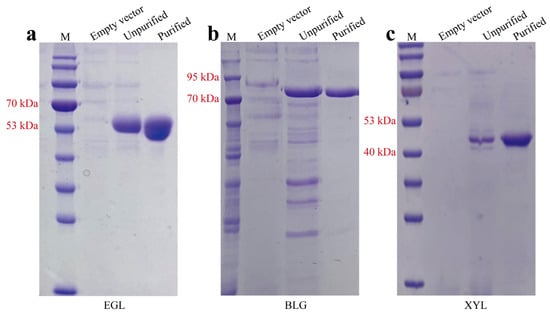
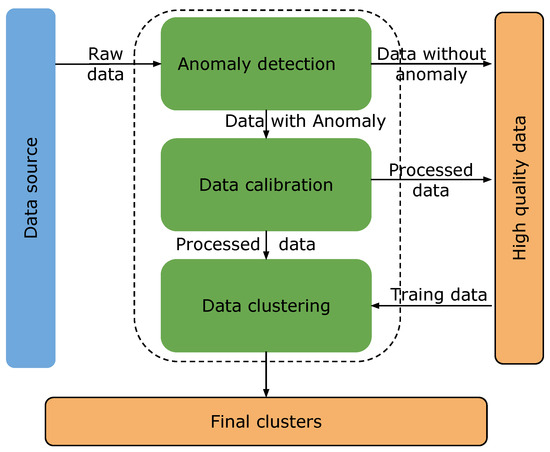
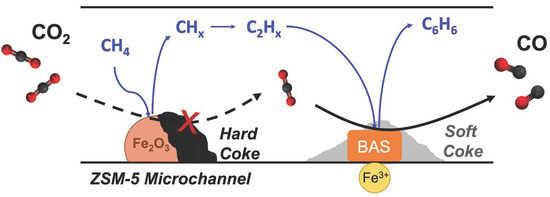
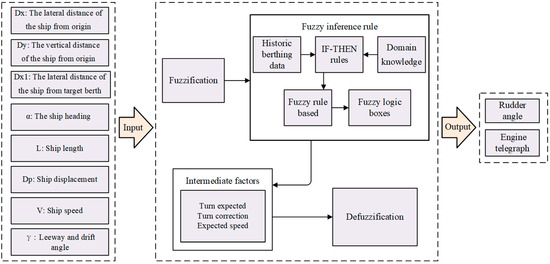
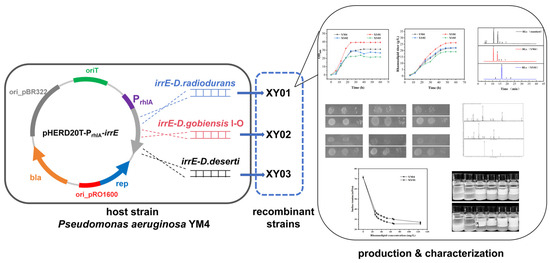
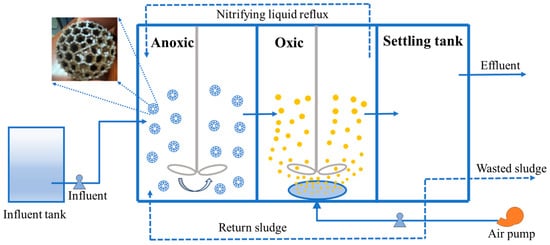
Ginkgo biloba L. leaves are rich in secondary metabolites with important medicinal values; to increase their contents, foliar spraying of micronutrients is a potential strategy. Zinc, a multifunctional element, has a significant impact on the content of secondary metabolites in other plants, but
[...] Read more.
Ginkgo biloba L. leaves are rich in secondary metabolites with important medicinal values; to increase their contents, foliar spraying of micronutrients is a potential strategy. Zinc, a multifunctional element, has a significant impact on the content of secondary metabolites in other plants, but relevant research into ginkgo is still lacking. In our study, different spraying time and concentration strategies were used to investigate the effects of zinc sulfate (ZnSO
4) on physiological indicators and secondary metabolites of 2-year-old ginkgo. The results demonstrated that ZnSO
4 could increase the contents of hydrogen peroxide, abscisic acid, and free amino acids in ginkgo leaves. It also enhances the antioxidant enzyme activity of ginkgo leaves, decreases the content of plant auxin, and ultimately facilitates the accumulation of ginkgo terpene lactones (TTL). Spraying ZnSO
4 in June resulted in a more significant increase in the contents of TTL and flavonoids compared to spraying in August. After spraying 12 mmol/L ZnSO
4 in June, the contents of TTL and flavonoids in ginkgo leaves were significantly elevated by 35.95% and 24.30%, respectively, compared to those in the CK (
p < 0.05). The contents of ginkgolide A, B, and C were notably increased by 45.93%, 46.56%, and 74.29%, respectively, compared to those in the CK (
p < 0.05). Therefore, our study suggests that the optimal timing for spraying ZnSO
4 on ginkgo is in June, with a recommended concentration of 12 mmol/L. Our study provides a theoretical basis for the accumulation of secondary metabolites in ginkgo and guides the production of its leaf-utilization plantations.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT