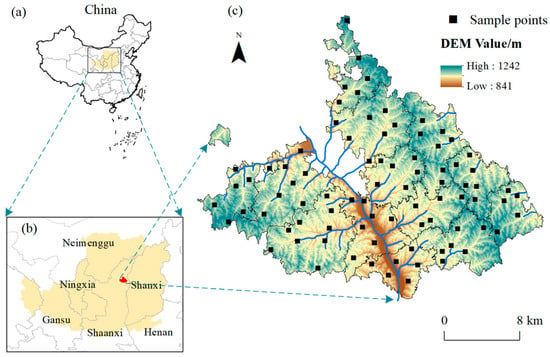
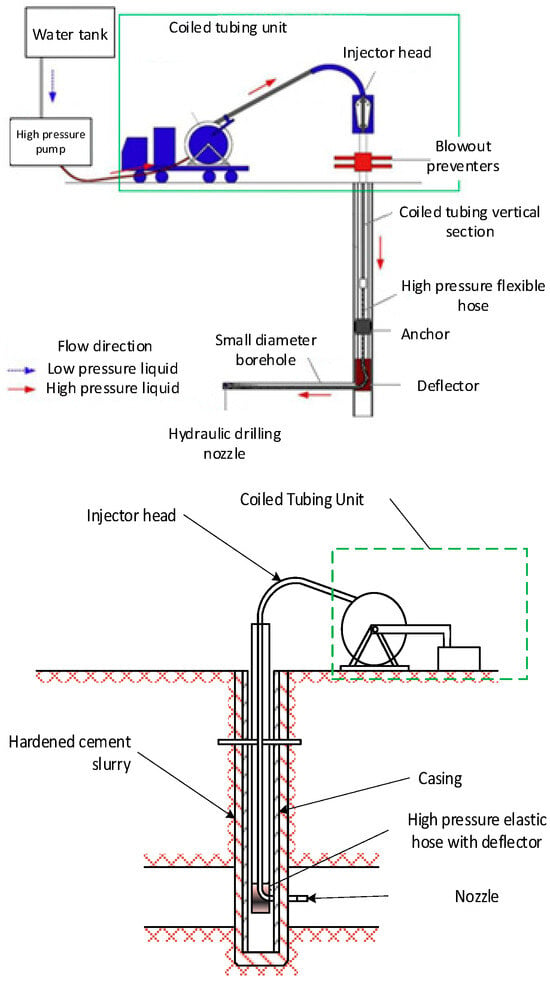
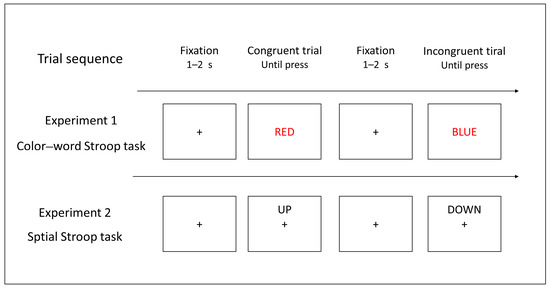
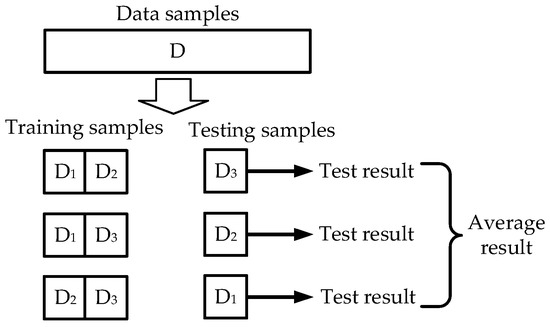
This investigation explores the structural and electronic properties of low-temperature-grown (InAs)
4(GaAs)
3/Be-doped InAlAs and InGaAs/Be-doped InAlAs multiple quantum wells (MQWs), utilizing migration-enhanced epitaxy (MEE) and conventional molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) growth mode. Through comprehensive characterization methods including transmission electron microscopy
[...] Read more.
This investigation explores the structural and electronic properties of low-temperature-grown (InAs)
4(GaAs)
3/Be-doped InAlAs and InGaAs/Be-doped InAlAs multiple quantum wells (MQWs), utilizing migration-enhanced epitaxy (MEE) and conventional molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) growth mode. Through comprehensive characterization methods including transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy (AFM), pump–probe transient reflectivity, and Hall effect measurements, the study reveals significant distinctions between the two types of MQWs. The (InAs)
4(GaAs)
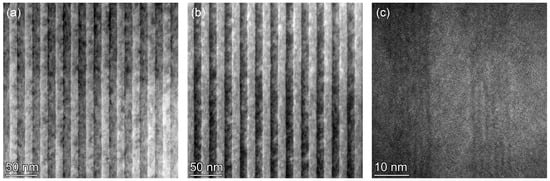
3/Be-doped InAlAs MQWs grown via the MEE mode exhibit enhanced periodicity and interface quality over the InGaAs/Be-InAlAs MQWs grown through the conventional molecule beam epitaxy (MBE) mode, as evidenced by TEM. The AFM results indicate lower surface roughness for the (InAs)
4(GaAs)
3/Be-doped InAlAs MQWs by using the MEE mode. Raman spectroscopy reveals weaker disorder-activated modes in the (InAs)
4(GaAs)
3/Be-doped InAlAs MQWs by using the MEE mode. This originates from utilizing the (InAs)
4(GaAs)
3 short period superlattices rather than InGaAs, which suppresses the arbitrary distribution of Ga and In atoms during the InGaAs growth. Furthermore, pump–probe transient reflectivity measurements show shorter carrier lifetimes in the (InAs)
4(GaAs)
3/Be-doped InAlAs MQWs, attributed to a higher density of antisite defects. It is noteworthy that room temperature Hall measurements imply that the mobility of (InAs)
4(GaAs)
3/Be-doped InAlAs MQWs grown at a low temperature of 250 °C via the MEE mode is superior to that of InGaAs/Be-doped InAlAs MQWs grown in the conventional MBE growth mode, reaching 2230 cm
2/V.s. The reason for the higher mobility of (InAs)
4(GaAs)
3/Be-doped InAlAs MQWs is that this short-period superlattice structure can effectively suppress alloy scattering caused by the arbitrary distribution of In and Ga atoms during the growth process of the InGaAs ternary alloy. These results exhibit the promise of the MEE growth approach for growing high-performance MQWs for advanced optoelectronic applications, notably for high-speed optoelectronic devices like THz photoconductive antennas.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT