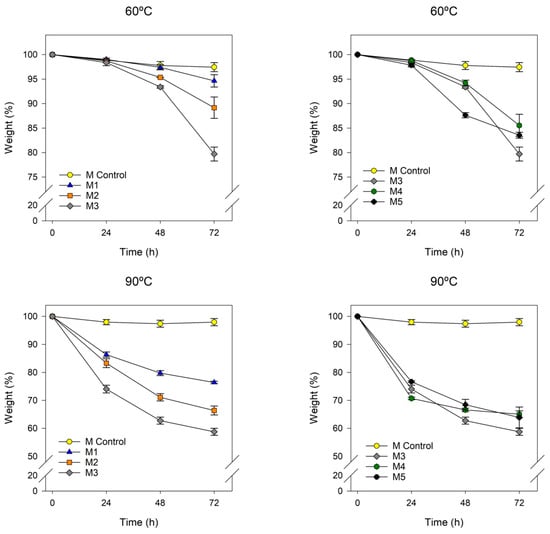
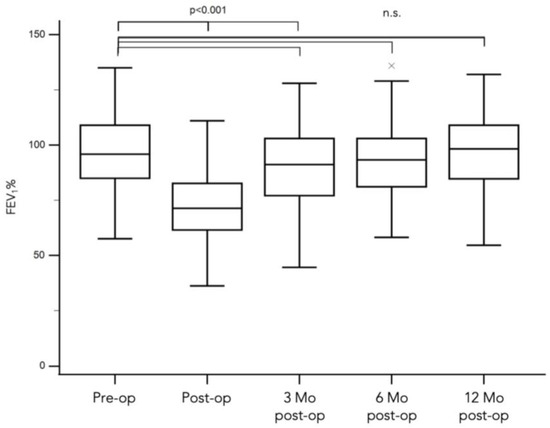
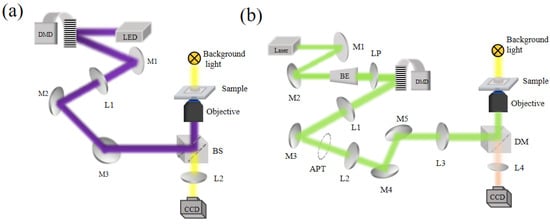
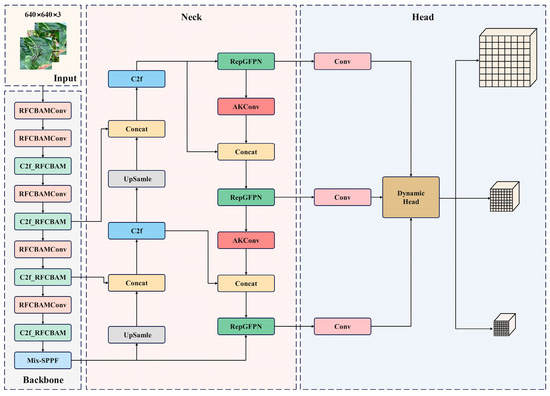
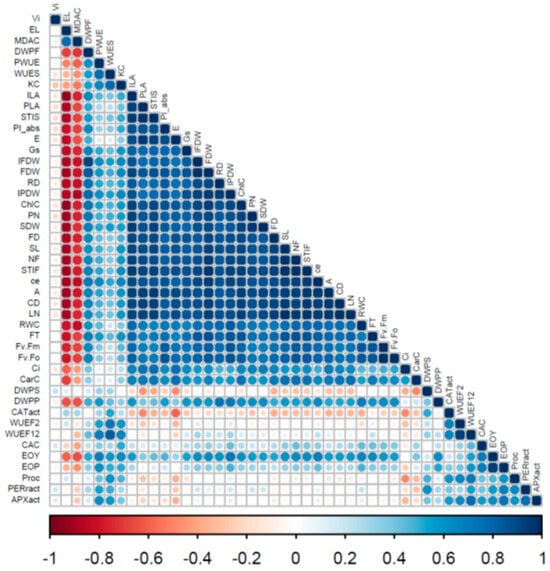
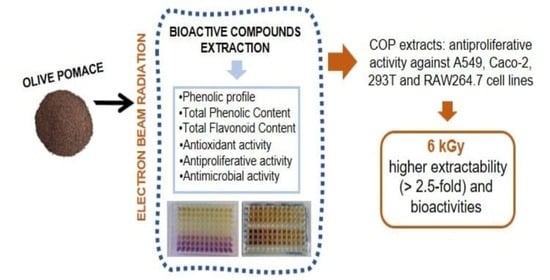
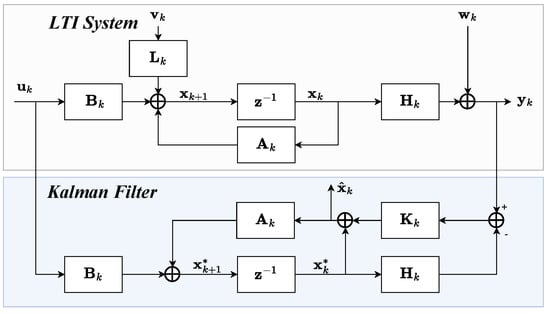
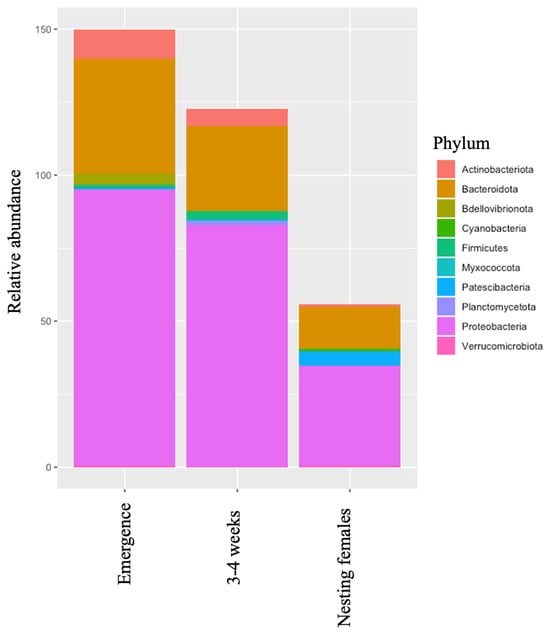
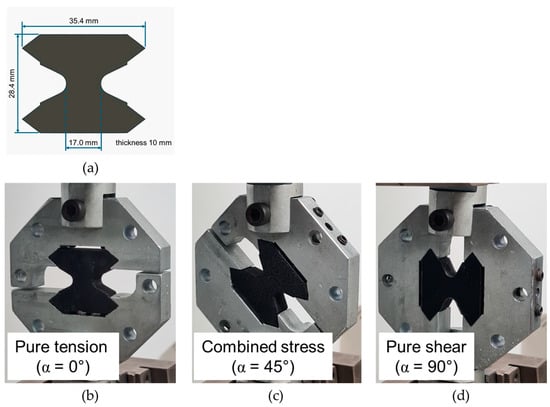
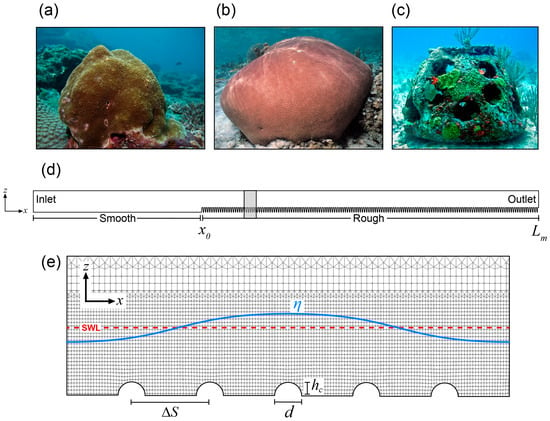
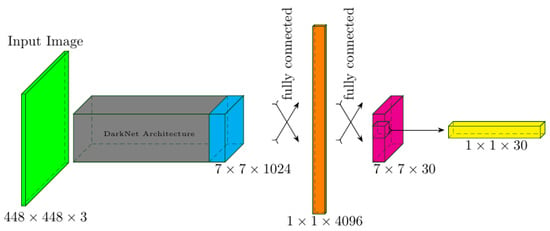
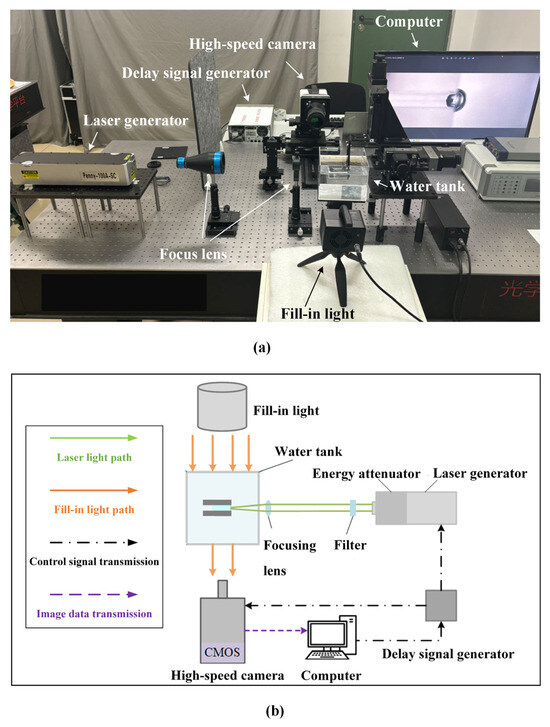
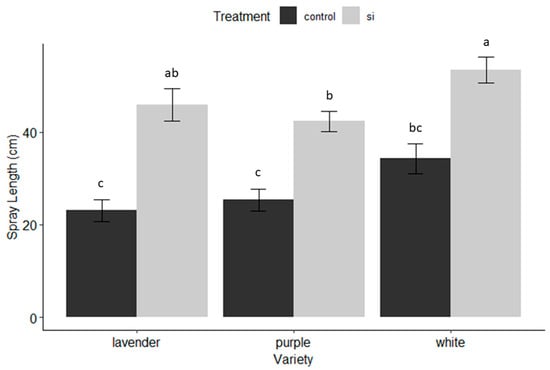
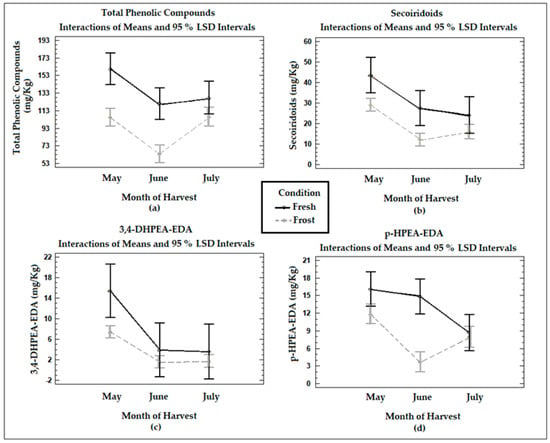
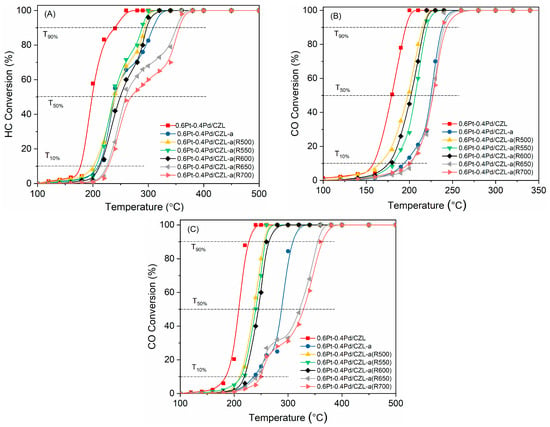
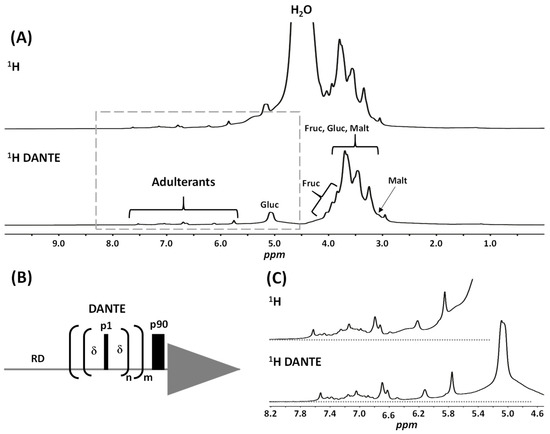
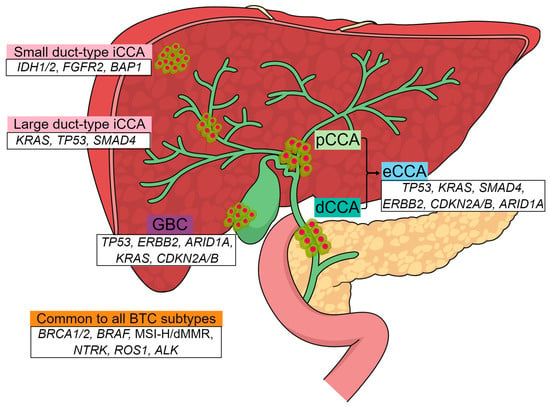
Background: Assessment of potential lymph node metastasis is mandatory in the appropriate treatment of early gastric cancers. This study analysed factors associated with lymph node metastasis to identify differences between node-negative and node-positive patients and between T1a and T1b cancers.
Methods: The clinicopathological features of 129 early gastric cancer patients who had undergone radical gastrectomy were analysed to identify predictive factors for lymph node metastasis.
Results: Lymph node metastasis was detected in 76 (59.0%) patients. Node-positive patients were younger (58.1 ± 11.3 years) than those without metastasis (61.9 ± 9.6 years,
p = 0.02). Greater tumour sizes were observed in patients with lymph node metastasis (3.6 ± 1.0 cm) compared to node-negative patients (1.9 ± 0.5 cm,
p = 0.00001). Depressed form, ulceration, diffuse histological type, and undifferentiated lesions were more frequent in node-positive patients than in the node-negative group. Tumour size > 3.0 cm showed a correlation with lymph node metastasis in both T1a (
p = 0.0001) and T1b (
p = 0.006) cancer. The male sex (
p = 0.006) had a significant correlation with lymph node metastasis in T1a cancer. Depressed appearance (
p = 0.02), ulceration (
p = 0.03), differentiation (
p = 0.0001), diffuse type (
p = 0.0002), and lower third location (
p = 0.005) were associated with lymph node metastasis in T1b cancer.
Conclusions: Tumour size > 3 cm, undifferentiated lesions, ulceration, diffuse type, lower third location, and submucosal invasion are risk factors for lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT