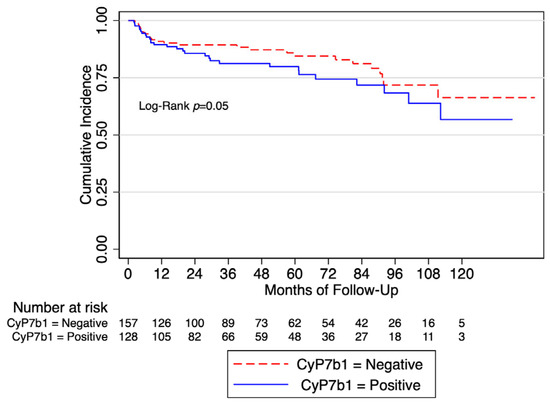
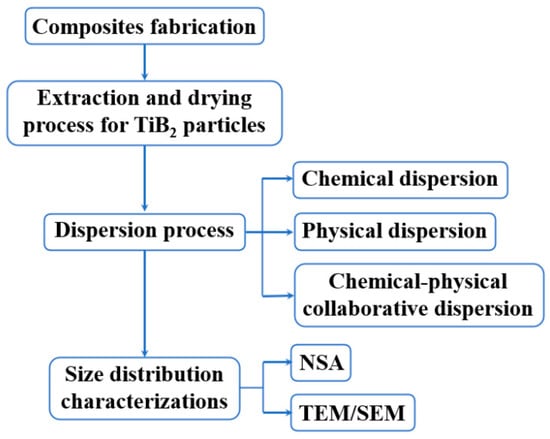
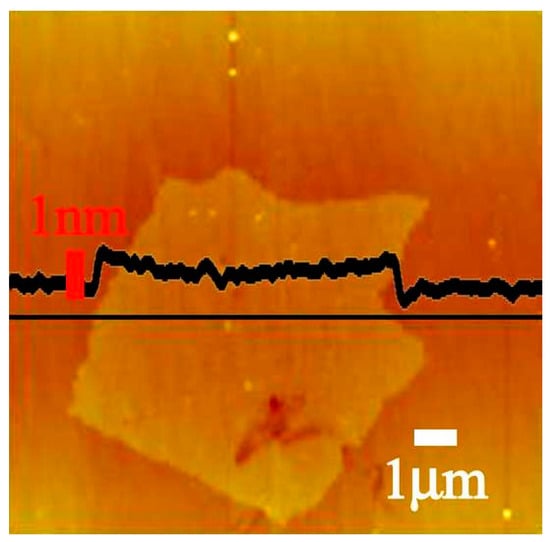
The wide size range and high tendency to agglomerate of in-situ TiB
2 particles in reinforced Al matrix composites introduce great difficulties in their size characterization. In order to use a nanoparticle size analyzer (NSA) to obtain the precise size distribution of TiB
2 particles, a controlled size characterization process has been explored. First, the extraction and drying processes for TiB
2 particles were optimized. In the extraction process, alternated applications of magnetic stirring and normal ultrasound treatments were proven to accelerate the dissolution of the Al matrix in HCl solution. Furthermore, freeze-drying was found to minimize the agglomeration tendency among TiB
2 particles, facilitating the acquisition of pure powders. Such powders were quantitatively made into an initial TiB
2 suspension. Second, the chemical and physical dispersion technologies involved in initial TiB
2 suspension were put into focus. Chemically, adding PEI (M.W. 10000) at a ratio of m
PEI/m
TiB2 = 1/30 into the initial suspension can greatly improve the degree of TiB
2 dispersion. Physically, the optimum duration for high-energy ultrasound application to achieve TiB
2 dispersion was 10 min. Overall, the corresponding underlying dispersion mechanisms were discussed in detail. With the combination of these chemical and physical dispersion specifications for TiB
2 suspension, the bimodal size distribution of TiB
2 was able to be characterized by NSA for the first time, and its number-average diameter was 111 ± 6 nm, which was reduced by 59.8% over the initial suspension. Indeed, the small-sized and large-sized peaks of the TiB
2 particles characterized by NSA mostly match the results obtained from transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy, respectively.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT