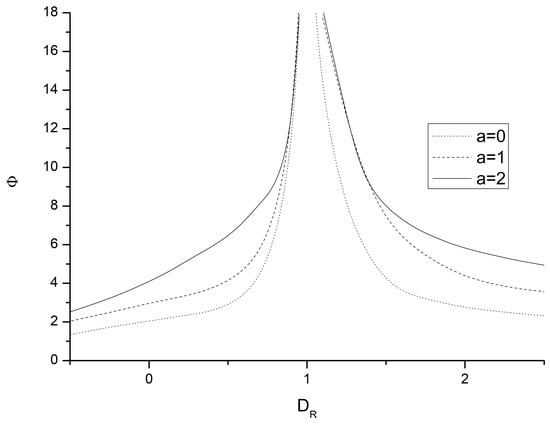
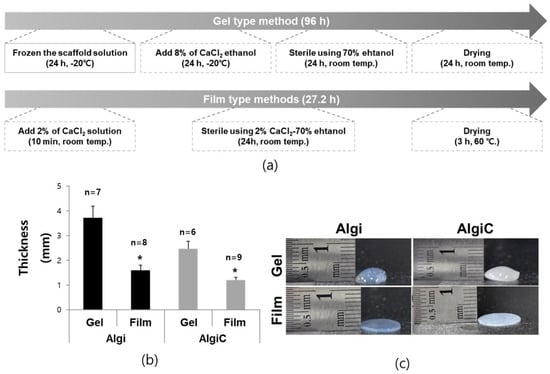
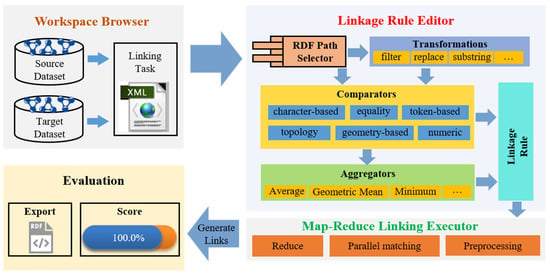
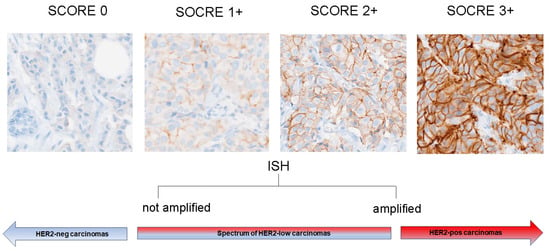
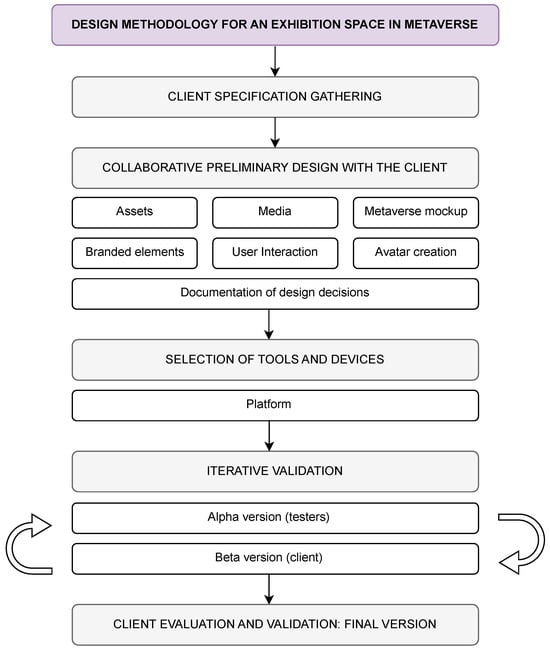
With this follow-up paper, we continue developing a mathematical framework based on information geometry for representing physical objects. The long-term goal is to lay down informational foundations for physics, especially quantum physics. We assume that we can now model information sources as univariate normal probability distributions
, as before, but with a constant
not necessarily equal to 1. Then, we also relaxed the independence condition when modeling
m sources of information. Now, we model
m sources with a multivariate normal probability distribution
with a constant variance–covariance matrix
not necessarily diagonal, i.e., with covariance values different to 0, which leads to the concept of modes rather than sources. Invoking Schrödinger’s equation, we can still break the information into
m quantum harmonic oscillators, one for each mode, and with energy levels independent of the values of
, altogether leading to the concept of “intrinsic”. Similarly, as in our previous work with the estimator’s variance, we found that the expectation of the quadratic Mahalanobis distance to the sample mean equals the energy levels of the quantum harmonic oscillator, being the minimum quadratic Mahalanobis distance at the minimum energy level of the oscillator and reaching the “intrinsic” Cramér–Rao lower bound at the lowest energy level. Also, we demonstrate that the global probability density function of the collective mode of a set of
m quantum harmonic oscillators at the lowest energy level still equals the posterior probability distribution calculated using Bayes’ theorem from the sources of information for all data values, taking as a prior the Riemannian volume of the informative metric. While these new assumptions certainly add complexity to the mathematical framework, the results proven are invariant under transformations, leading to the concept of “intrinsic” information-theoretic models, which are essential for developing physics.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT