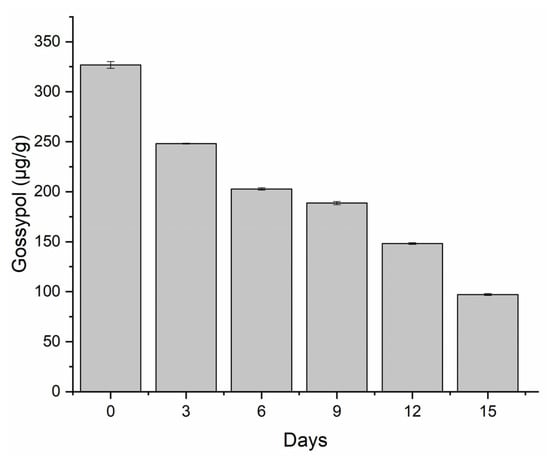
Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) is one of the main pathogens that can negatively affect soybean production and quality. To study the gene regulatory network of soybeans in response to SMV SC15, the resistant line X149 and susceptible line X97 were subjected to transcriptome analysis at 0, 2, 8, 12, 24, and 48 h post-inoculation (hpi). Differential expression analysis revealed that 10,190 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) responded to SC15 infection. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was performed to identify highly related resistance gene modules; in total, eight modules, including 2256 DEGs, were identified. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of 2256 DEGs revealed that the genes significantly clustered into resistance-related pathways, such as the plant–pathogen interaction pathway, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling pathway, and plant hormone signal transduction pathway. Among these pathways, we found that the flg22, Ca
2+, hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2), and abscisic acid (ABA) regulatory pathways were fully covered by 36 DEGs. Among the 36 DEGs, the gene
Glyma.01G225100 (protein phosphatase 2C, PP2C) in the ABA regulatory pathway, the gene
Glyma.16G031900 (WRKY transcription factor 22, WRKY22) in Ca
2+ and H
2O
2 regulatory pathways, and the gene
Glyma.04G175300 (calcium-dependent protein kinase, CDPK) in Ca
2+ regulatory pathways were highly connected hub genes. These results indicate that the resistance of X149 to SC15 may depend on the positive regulation of flg22, Ca
2+, H
2O
2, and ABA regulatory pathways. Our study further showed that superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, H
2O
2 content, and catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD) activities were significantly up-regulated in the resistant line X149 compared with those in 0 hpi. This finding indicates that the H
2O
2 regulatory pathway might be dependent on flg22- and Ca
2+-pathway-induced ROS generation. In addition, two hub genes,
Glyma.07G190100 (encoding F-box protein) and
Glyma.12G185400 (encoding calmodulin-like proteins, CMLs), were also identified and they could positively regulate X149 resistance. This study provides pathways for further investigation of SMV resistance mechanisms in soybean.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT