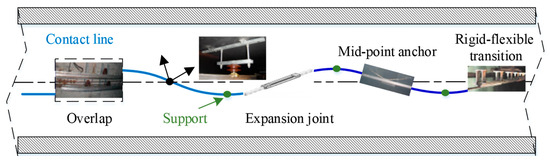
The separation of rare earth ions (RE
3+) from aqueous solutions poses a significant challenge due to their similar chemical and physical characteristics. This study presents a method for synthesizing hematite nanoparticles (Fe
2O
3 NPs) through the high-temperature phase transition
[...] Read more.
The separation of rare earth ions (RE
3+) from aqueous solutions poses a significant challenge due to their similar chemical and physical characteristics. This study presents a method for synthesizing hematite nanoparticles (Fe
2O
3 NPs) through the high-temperature phase transition of natural pyrite for adsorbing RE
3+ from mine wastewater. The characteristics of Fe
2O
3 NPs were studied using XRD, SEM, BET, XPS, FTIR, and Zeta potential. The optimal condition for RE
3+ adsorption by Fe
2O
3 NPs was determined to be at pH 6.0 with an adsorption time of 60 min. The maximum adsorption capacities of Fe
2O
3 NPs for La
3+, Ce
3+, Pr
3+, Nd
3+, Sm
3+, Gd
3+, Dy
3+, and Y
3+ were 12.80, 14.02, 14.67, 15.52, 17.66, 19.16, 19.94, and 11.82 mg·g
−1, respectively. The experimental data fitted well with the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order models, suggesting that the adsorption process was dominated by monolayer chemisorption. Thermodynamic analysis revealed the endothermic nature of the adsorption process. At room temperature, the adsorption of RE
3+ in most cases (La
3+, Ce
3+, Pr
3+, Nd
3+, Sm
3+, and Y
3+) onto Fe
2O
3 NPs was non-spontaneous, except for the adsorption of Gd
3+ and Dy
3+, which was spontaneous. The higher separation selectivity of Fe
2O
3 NPs for Gd
3+ and Dy
3+ was confirmed by the separation factor. Moreover, Fe
2O
3 NPs exhibited excellent stability, with an RE
3+ removal efficiency exceeding 94.70% after five adsorption–desorption cycles, demonstrating its potential for the recovery of RE
3+ from mine wastewater.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT