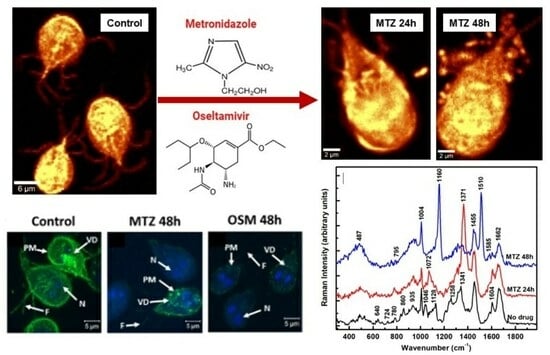
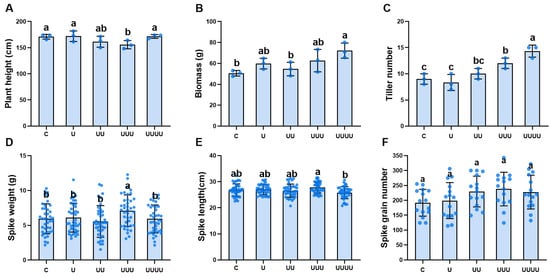
Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer management can effectively improve soil ecology, promote agricultural production, and increase the income of farmers and workers. Nitrogen fertilizer is an important factor in the growth and development of rice, and it is important to find out the optimal amount
[...] Read more.
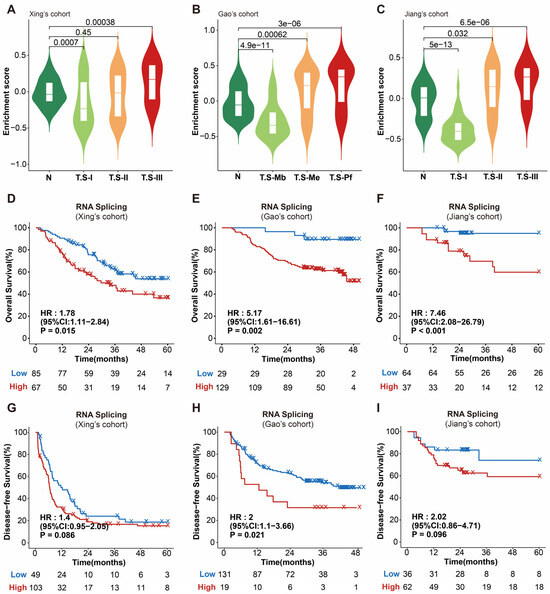
Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer management can effectively improve soil ecology, promote agricultural production, and increase the income of farmers and workers. Nitrogen fertilizer is an important factor in the growth and development of rice, and it is important to find out the optimal amount and frequency of fertilizer application for the super-hybrid early rice ‘Zhu LiangYou 819’ in Hunan Province, to give full play to its high quality and high yield characteristics. Various N fertilizer application frequencies (P1, basal–tiller fertilizer = 5:5; P2, basal–tiller–spike fertilizer = 4:3:3; P3, basal–tiller–spike–grain fertilizer = 4:3:2:1) and N application amounts (N1, 90 kg ha
−1; N2, 150 kg ha
−1; N3, 210 kg ha
−1) were applied to the hybrid rice ZLY819. The results show that, under the same frequency of N application, ZLY819 had the highest yield, agronomic efficiency, and physiological utilization rate of N fertilizer with the N2 treatment, averaging 7.53 t ha
−1, 18.10 kg kg
−1, and 34.34%, respectively, with the yield under N2 being 19.38% higher than that under N1. For the same amount of N application, the yield, agronomic efficiency, partial factor productivity of N (PFPN), N contribution to seed, and N use efficiency (NUE) increased with an increase in the frequency of N application, mainly in the order of P3 > P2 > P1, whereby the yield of P3 was 10.11% higher than that of P1. According to the regression equation, the yield is higher when the amount of nitrogen application is 202.15 kg ha
−1 and the fertilization frequency is four times. Appropriate N fertilizer management (P3N2) improved the rice growth characteristics, dry matter accumulation, crop growth rate, dry matter transport rate, dry matter contribution rate, and NUE, thus promoting an increase in the rice yield and efficient use of nitrogen.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT