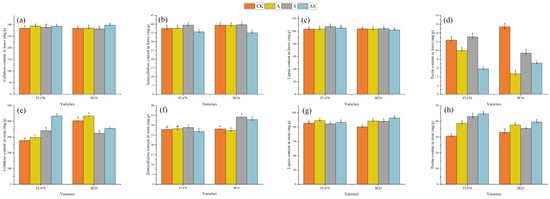
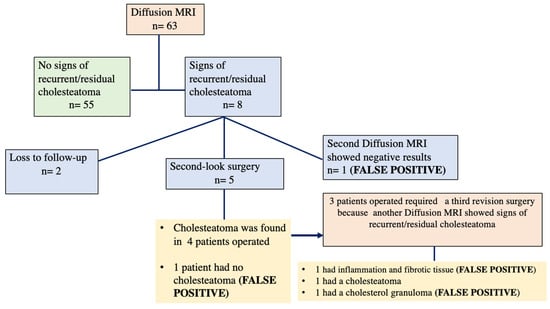
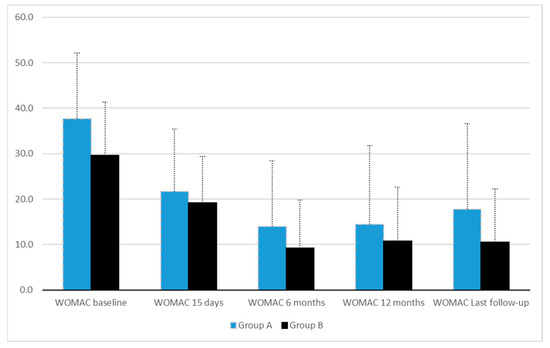
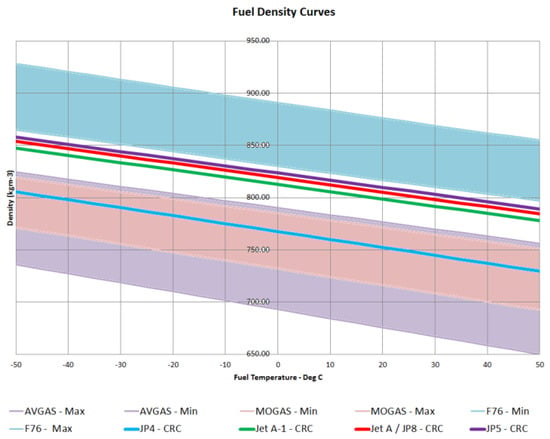
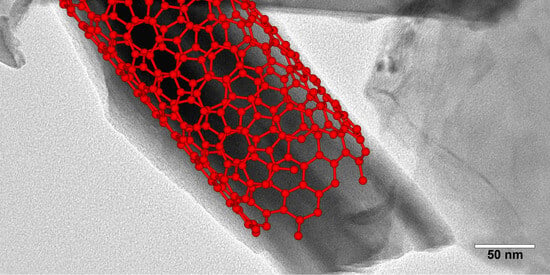
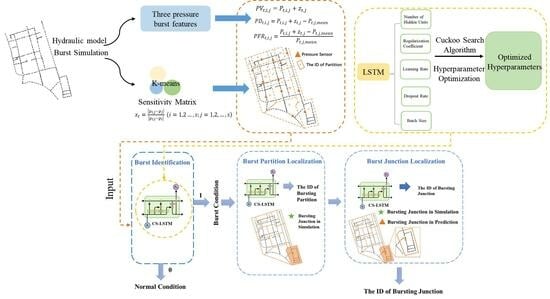
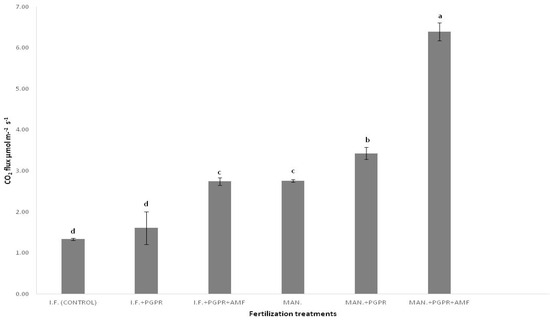
The current study aimed to quantify the value of color spaces and channels as a potential superior replacement for standard grayscale images, as well as the relative performance of open-source detectors and descriptors for general feature-based image registration purposes, based on a large benchmark dataset. The public dataset UDIS-D, with 1106 diverse image pairs, was selected. In total, 21 color spaces or channels including RGB, XYZ, Y′CrCb, HLS, L*a*b* and their corresponding channels in addition to grayscale, nine feature detectors including AKAZE, BRISK, CSE, FAST, HL, KAZE, ORB, SIFT, and TBMR, and 11 feature descriptors including AKAZE, BB, BRIEF, BRISK, DAISY, FREAK, KAZE, LATCH, ORB, SIFT, and VGG were evaluated according to reprojection error (RE), root mean square error (RMSE), structural similarity index measure (SSIM), registration failure rate, and feature number, based on 1,950,984 image registrations. No meaningful benefits from color space or channel were observed, although XYZ, RGB color space and L* color channel were able to outperform grayscale by a very minor margin. Per the dataset, the best-performing color space or channel, detector, and descriptor were XYZ/RGB, SIFT/FAST, and AKAZE. The most robust color space or channel, detector, and descriptor were L*a*b*, TBMR, and VGG. The color channel, detector, and descriptor with the most initial detector features and final homography features were Z/L*, FAST, and KAZE. In terms of the best overall unfailing combinations, XYZ/RGB+SIFT/FAST+VGG/SIFT seemed to provide the highest image registration quality, while Z+FAST+VGG provided the most image features.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT