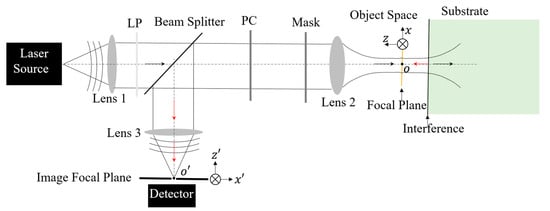
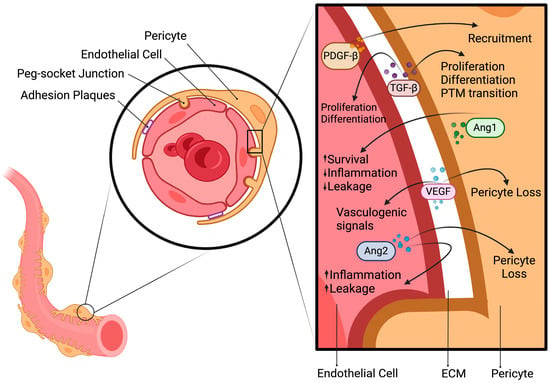
The blackberry, valued for its delicious fruit, has gained attention for its medicinal bioactive compounds. In vitro cultivation methods, including nanoparticle enhancement, are increasingly chosen due to their advantages over traditional propagation techniques. We tested the effect of commercial zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs)
[...] Read more.
The blackberry, valued for its delicious fruit, has gained attention for its medicinal bioactive compounds. In vitro cultivation methods, including nanoparticle enhancement, are increasingly chosen due to their advantages over traditional propagation techniques. We tested the effect of commercial zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) on the growth and development of blackberry (
Rubus fruticosus L.) of the Navaho variety in an in vitro culture on MS medium supplemented with 0.6 mg dm
−3 BA, 0.1 mg dm
−3 IBA, 0.01 mg dm
−3 GA
3, and various concentrations of zinc oxide nanoparticles: 0 (control), 10, 20, 30, and 40 mg dm
−3. The morphological features of the plantlets were assessed two and three months after the start of the culture. Selected biological characteristics of the plantlets were determined. The values of the morphological and biological parameters assessed in the plantlets from in vitro culture depended on the concentration of ZnONPs in the medium. Increasing the concentration of ZnONPs negatively affected the number and length of shoots and roots and the fresh weight of the plantlets. The total phenolic content in the plantlets from the treatments with ZnONPs was lower than in the control plants, but the total antioxidant capacity as measured by the ABTS method was higher. The content of chlorophyll
a, chlorophyll
b, total chlorophyll, and carotenoids in the blackberry plantlets decreased at higher concentrations of ZnONPs in the medium. The addition of zinc oxide nanoparticles increased the zinc content and reduced the iron content in the blackberry plantlets. Concentrations of 10–30 mg dm
−3 ZnONPs increased the concentrations of potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, manganese, and copper, while at the highest concentration of 40 mg dm
−3 ZnONPs, the concentrations of these minerals were similar to the control, except for a lower content of calcium and manganese. The plantlets from the in vitro culture growing in the presence of ZnONPs were acclimatized to ex vitro conditions in control soil and soil inoculated with
Bacillus thuringiensis. Bacteria added to the ex vitro substrate favourably influenced the growth and development of the shoots and roots of the blackberry plants and their fresh weight.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT