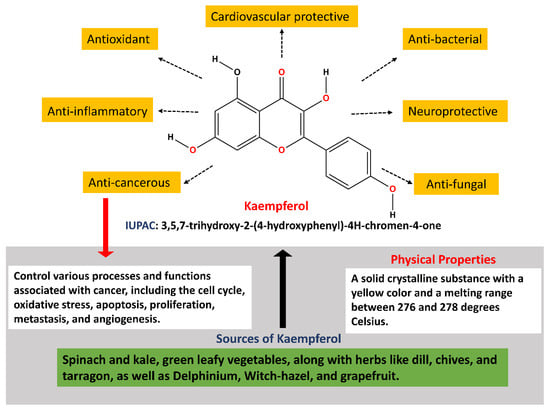
α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are mainly distributed in the central nervous system (CNS), including the hippocampus, striatum, and cortex of the brain. The
α7 nAChR has high Ca
2+ permeability and can be quickly activated and desensitized, and is closely related to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), epilepsy, schizophrenia, lung cancer, Parkinson’s disease (PD), inflammation, and other diseases. α-conotoxins from marine cone snail venom are typically short, disulfide-rich neuropeptides targeting nAChRs and can distinguish various subtypes, providing vital pharmacological tools for the functional research of nAChRs. [Q1G, ΔR14]LvΙB is a rat
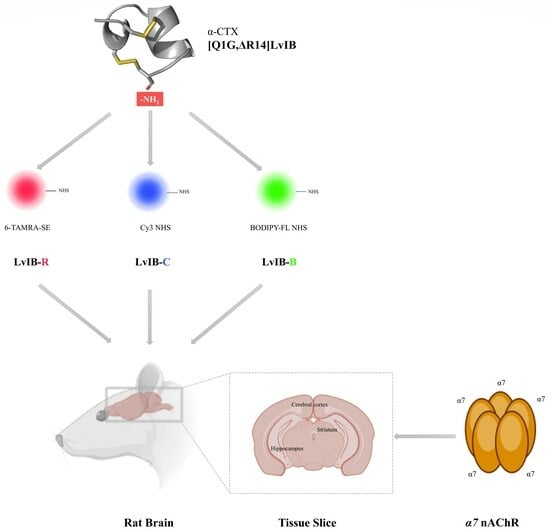
α7 nAChRs selective antagonist, modified from α-conotoxin LvΙB. In this study, we utilized three types of fluorescein after N-Hydroxy succinimide (NHS) activation treatment: 6-TAMRA-SE, Cy3 NHS, and BODIPY-FL NHS, labeling the N-Terminal of [Q1G, ΔR14]LvΙB under weak alkaline conditions, obtaining three fluorescent analogs: LvIB-R, LvIB-C, and LvIB-B, respectively. The potency of [Q1G, ΔR14]LvΙB fluorescent analogs was evaluated at rat
α7 nAChRs expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes. Using a two-electrode voltage clamp (TEVC), the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC
50) values of LvIB-R, LvIB-C, and LvIB-B were 643.3 nM, 298.0 nM, and 186.9 nM, respectively. The stability of cerebrospinal fluid analysis showed that after incubation for 12 h, the retention rates of the three fluorescent analogs were 52.2%, 22.1%, and 0%, respectively. [Q1G, ΔR14]LvΙB fluorescent analogs were applied to explore the distribution of
α7 nAChRs in the hippocampus and striatum of rat brain tissue and it was found that Cy3- and BODIPY FL-labeled [Q1G, ΔR14]LvΙB exhibited better imaging characteristics than 6-TAMARA-. It was also found that
α7 nAChRs are widely distributed in the cerebral cortex and cerebellar lobules. Taking into account potency, imaging, and stability, [Q1G, ΔR14]LvΙB -BODIPY FL is an ideal pharmacological tool to investigate the tissue distribution and function of
α7 nAChRs. Our findings not only provide a foundation for the development of conotoxins as visual pharmacological probes, but also demonstrate the distribution of
α7 nAChRs in the rat brain.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT