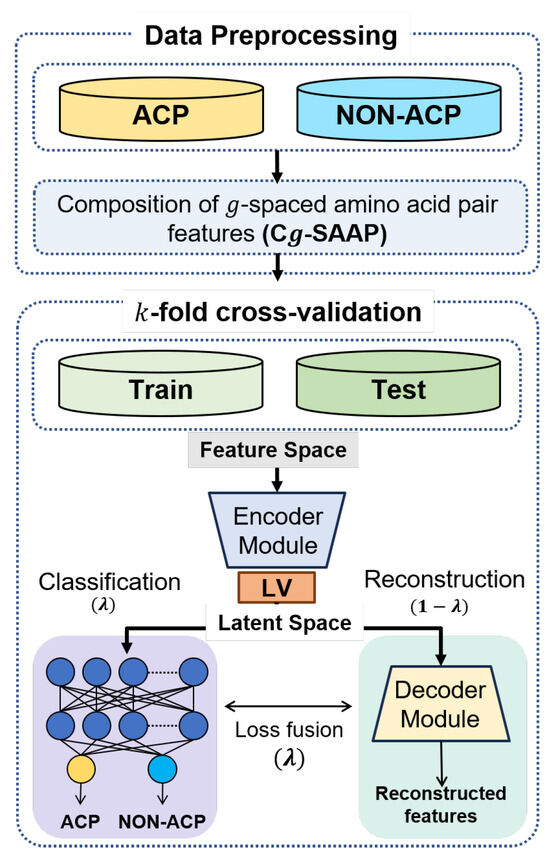
Background and objectives: Diabetic foot stands out as one of the most consequential and devastating complications of diabetes. Many factors, including VIPS (Vascular management, Infection management, Pressure relief, and Source of healing), influence the prognosis and treatment of diabetic foot patients. There
[...] Read more.
Background and objectives: Diabetic foot stands out as one of the most consequential and devastating complications of diabetes. Many factors, including VIPS (Vascular management, Infection management, Pressure relief, and Source of healing), influence the prognosis and treatment of diabetic foot patients. There are many studies on VIPS, but relatively few studies on “sources of healing”. Nutrients that affect wound healing are known, but objective data in diabetic foot patients are insufficient. We hypothesized that “sources of healing” would have many effects on wound healing. The purpose of this study is to know the affecting factors related to the source of healing for diabetic foot patients.
Materials and Methods: A retrospective review identified 46 consecutive patients who were admitted for diabetic foot management from July 2019 to April 2021 at our department. Several laboratory tests were performed for influencing factor evaluation. We checked serum levels of total protein, albumin, vitamin B, iron, zinc, magnesium, copper, Hb, HbA1c, HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol. These values of diabetic foot patients were compared with normal values. Patients were divided into two groups based on wound healing rate, age, length of hospital stay, and sex, and the test values between the groups were compared.
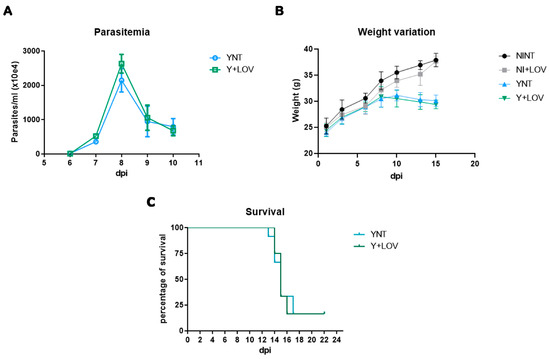
Results: Levels of albumin (37%) and Hb (89%) were low in the diabetic foot patients. As for trace elements, levels of iron (97%) and zinc (95%) were low in the patients, but levels of magnesium and copper were usually normal or high. There were no differences in demographic characteristics based on wound healing rate. However, when compared to normal adult values, diabetic foot patients in our data exhibited significantly lower levels of hemoglobin, total protein, albumin, iron, zinc, copper, and HDL cholesterol. When compared based on age and length of hospital stay, hemoglobin levels were significantly lower in both the older age group and the group with longer hospital stays.
Conclusions: Serum levels of albumin, Hb, iron, and zinc were very low in most diabetic foot patients. These low values may have a negative relationship with wound healing. Nutrient replacements are necessary for wound healing in diabetic foot patients.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT